Gardenia jasminoides protects against cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 18985809
- PMCID: PMC2761580
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.6188
Gardenia jasminoides protects against cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of Gardenia jasminoides (GJ) on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis (AP) in mice.
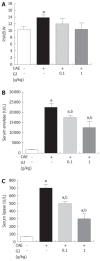
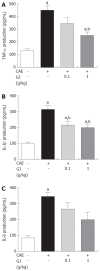
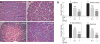
Methods: C57BL/6 mice weighing 18-20 g were divided into three groups. (1) Normal saline-treated group, (2) treatment with GJ at a dose of 0.1 g/kg, (3) treatment with GJ at a dose of 1 g/kg. GJ was administered orally (n = 6 per group) for 1 wk. Three hours later, the mice were given an intraperitoneal injection of cerulein (50 microg/kg), a stable cholecystokinin (CCK) analogue, every hour for a total of 6 h as described previously. The mice were sacrificed at 6 h after completion of cerulein injections. Blood samples were obtained to determine serum amylase, lipase and cytokine levels. The pancreas was rapidly removed for morphologic examination and scoring. A portion of pancreas was stored at -70 degree and prepared for the measurement of tissue myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, an indicator of neutrophil sequestration, and for reverse-transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) and real-time PCR measurements.
Results: Treatment with GJ decreased significantly the severity of pancreatitis and pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Treatment with GJ attenuated the severity of AP compared with saline-treated mice, as shown by reduction in pancreatic edema, neutrophil infiltration, serum amylase and lipase levels, serum cytokine levels, and mRNA expression of multiple inflammatory mediators.
Conclusion: These results suggest that GJ attenuated the severity of AP as well as pancreatitis-associated lung injury.
Figures
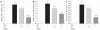

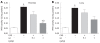
References
-
- Banks PA. Medical management of acute pancreatitis and complications. In: Go VLW, DiMagno EP, Gardner JD, Lebenthal E, Reber HA, et al., editors. The pancreas: biology, pathobiology, and disease. New York: Raven; 1993. pp. 593–611.
-
- Rau B, Uhl W, Buchler MW, Beger HG. Surgical treatment of infected necrosis. World J Surg. 1997;21:155–161. - PubMed
-
- Baron TH, Morgan DE. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1412–1417. - PubMed
-
- Ho HS, Frey CF. Gastrointestinal and pancreatic complications associated with severe pancreatitis. Arch Surg. 1995;130:817–822; discussion 822-823. - PubMed
-
- Norman J. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1998;175:76–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

