Effect of the phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil on rat anococcygeus muscle: functional and biochemical aspects
- PMID: 18986324
- PMCID: PMC3022481
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05071.x
Effect of the phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil on rat anococcygeus muscle: functional and biochemical aspects
Abstract
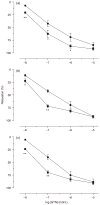
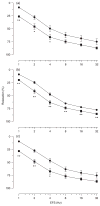
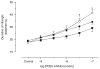
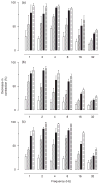
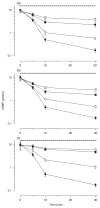
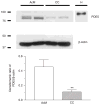
1. The anococcygeus muscle is part of the erectile machinery in male rodents. Phosphodiesterase (PDE) 5 inhibitors enhance and prolong the effects of cGMP, which has a key role in penile erection. The aim of the present study was to provide a functional and biochemical comparison of the three PDE5 inhibitors, namely sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil, in the rat anococcygeus muscle. 2. Muscle strips were mounted in 4 mL organ baths and isometric force recorded. Levels of cGMP were measured using an enzyme immunoassay kit. Western blots were used to determine PDE5 protein expression. 3. The PDE5 inhibitors concentration-dependently relaxed carbachol-precontracted anococcygeus muscle; however, vardenafil was more potent (pEC(50) = 8.11 +/- 0.05) than sildenafil (7.72 +/- 0.06) or tadalafil (7.69 +/- 0.05). Addition of N(G)-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (100 micromol/L) or 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (10 micromol/L) to the organ baths caused significant rightward shifts in concentration-response curves for all PDE5 inhibitors. 4. Sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil (all at 0.1 micromol/L) caused leftward shifts in the glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) concentration-response curves (by 4.0-, 3.7- and 5.5-fold, respectively). In addition, all three PDE5 inhibitors significantly potentiated relaxation responses to both GTN (0.01-10 micromol/L) and electrical field stimulation (EFS; 1-32 Hz), with vardenafil having more pronounced effects. 5. All three PDE5 inhibitors reduced EFS-evoked contractions in a concentration-dependent manner over the concentration range 0.001-1 micromol/L. There were no significant differences between the effects of the three PDE5 inhibitors. 6. Vardenafil (0.01-0.1 micromol/L) was more potent in preventing cGMP degradation in vitro than sildenafil (0.01-0.1 micromol/L) and tadalafil (0.01-0.1 micromol/L). 7. Under control conditions, the expression of PDE5 was higher in the anococcygeus muscle than in the corpus cavernosum. 8. In conclusion, PDE5 inhibitors enhance exogenous and endogenous nitric oxide-mediated relaxation in the rat anococcygeus muscle. The potency of vardenafil was greater than that of either sildenafil or tadalafil.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative relaxing effects of sildenafil, vardenafil, and tadalafil in human corpus cavernosum: contribution of endogenous nitric oxide release.Urology. 2009 Jul;74(1):216-21. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2008.12.056. Epub 2009 Apr 15. Urology. 2009. PMID: 19371941
-
Differential effects of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors sildenafil, vardenafil, and tadalafil in rat aorta.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Feb;316(2):654-61. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.092544. Epub 2005 Oct 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. PMID: 16204472
-
Mechanisms of direct relaxant effect of sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil on corpus cavernosum.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Jul 17;541(3):184-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.05.005. Epub 2006 May 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16777087
-
Overview of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition in erectile dysfunction.Am J Cardiol. 2003 Nov 6;92(9A):9M-18M. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(03)00824-5. Am J Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 14609619 Review.
-
Pharmacology and drug interaction effects of the phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors: focus on alpha-blocker interactions.Am J Cardiol. 2005 Dec 26;96(12B):42M-46M. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.07.011. Epub 2005 Dec 5. Am J Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 16387566 Review.
Cited by
-
Frequency-dependent characteristics of nerve-mediated ATP and acetylcholine release from detrusor smooth muscle.Exp Physiol. 2022 Apr;107(4):350-358. doi: 10.1113/EP090238. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Exp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35165960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson KE, Persson K. Nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide-mediated effects in lower urinary tract smooth muscles. World J Urol. 1994;12:274–80. - PubMed
-
- Gibson A. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors and nitrergic transmission: From zaprinast to sildenafil. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;411:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Toda N, Okamura T. The pharmacology of nitric oxide in the peripheral nervous system of blood vessels. Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55:271–324. - PubMed
-
- Andersson KE, Wagner G. Physiology of penile erection. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:191–236. - PubMed
-
- Andersson KE. Pharmacology of penile erection. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:417–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

