Integrated weighted gene co-expression network analysis with an application to chronic fatigue syndrome
- PMID: 18986552
- PMCID: PMC2625353
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-2-95
Integrated weighted gene co-expression network analysis with an application to chronic fatigue syndrome
Abstract
Background: Systems biologic approaches such as Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) can effectively integrate gene expression and trait data to identify pathways and candidate biomarkers. Here we show that the additional inclusion of genetic marker data allows one to characterize network relationships as causal or reactive in a chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) data set.
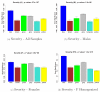
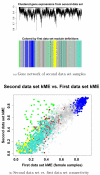
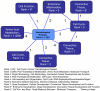
Results: We combine WGCNA with genetic marker data to identify a disease-related pathway and its causal drivers, an analysis which we refer to as "Integrated WGCNA" or IWGCNA. Specifically, we present the following IWGCNA approach: 1) construct a co-expression network, 2) identify trait-related modules within the network, 3) use a trait-related genetic marker to prioritize genes within the module, 4) apply an integrated gene screening strategy to identify candidate genes and 5) carry out causality testing to verify and/or prioritize results. By applying this strategy to a CFS data set consisting of microarray, SNP and clinical trait data, we identify a module of 299 highly correlated genes that is associated with CFS severity. Our integrated gene screening strategy results in 20 candidate genes. We show that our approach yields biologically interesting genes that function in the same pathway and are causal drivers for their parent module. We use a separate data set to replicate findings and use Ingenuity Pathways Analysis software to functionally annotate the candidate gene pathways.
Conclusion: We show how WGCNA can be combined with genetic marker data to identify disease-related pathways and the causal drivers within them. The systems genetics approach described here can easily be used to generate testable genetic hypotheses in other complex disease studies.
Figures



References
-
- Emilsson V, Thorleifsson G, Zhang B, Leonardson AS, Zink F, Zhu J, Carlson S, Helgason A, Walters GB, Gunnarsdottir S, Mouy M, Steinthorsdottir V, Eiriksdottir GH, Bjornsdottir G, Reynisdottir I, Gudbjartsson D, Helgadottir A, Jonasdottir A, Styrkarsdottir U, Gretarsdottir S, Magnusson KP, Stefansson H, Fossdal R, Kristjansson K, Gislason HG, Stefansson T, Leifsson BG, Thorsteinsdottir U, Lamb JR, Gulcher JR, Reitman ML, Kong A, Schadt EE, Stefansson K. Genetics of gene expression and its effect on disease. Nature. 2008;452:423–8. doi: 10.1038/nature06758. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

