Myogenic Akt signaling upregulates the utrophin-glycoprotein complex and promotes sarcolemma stability in muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 18986978
- PMCID: PMC2638781
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddn358
Myogenic Akt signaling upregulates the utrophin-glycoprotein complex and promotes sarcolemma stability in muscular dystrophy
Abstract
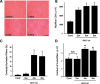
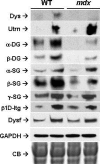
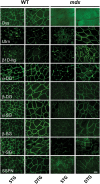
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is caused by dystrophin mutations that lead to structural instability of the sarcolemma membrane, myofiber degeneration/regeneration and progressive muscle wasting. Here we show that myogenic Akt signaling in mouse models of dystrophy promotes increased expression of utrophin, which replaces the function of dystrophin thereby preventing sarcolemma damage and muscle wasting. In contrast to previous suggestions that increased Akt in dystrophy was a secondary consequence of pathology, our findings demonstrate a pivotal role for this signaling pathway such that modulation of Akt can significantly affect disease outcome by amplification of existing, physiological compensatory mechanisms.
Figures
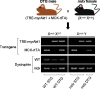
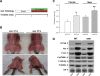
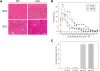
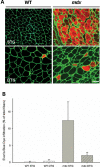
References
-
- Hoffman E.P., Brown R.H., Kunkel L.M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987;51:919–928. - PubMed
-
- Ervasti J.M., Ohlendieck K., Kahl S.D., Gaver M.G., Campbell K.P. Deficiency of a glycoprotein component of the dystrophin complex in dystrophic muscle. Nature. 1990;345:315–319. - PubMed
-
- Durbeej M., Campbell K.P. Muscular dystrophies involving the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex: an overview of current mouse models. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002;12:349–361. - PubMed
-
- Heydemann A., McNally E.M. Consequences of disrupting the dystrophin-sarcoglycan complex in cardiac and skeletal myopathy. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007;17:55–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

