Nicotinamide restores cognition in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice via a mechanism involving sirtuin inhibition and selective reduction of Thr231-phosphotau
- PMID: 18987186
- PMCID: PMC2617713
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3203-08.2008
Nicotinamide restores cognition in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice via a mechanism involving sirtuin inhibition and selective reduction of Thr231-phosphotau
Abstract
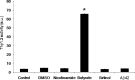
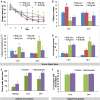
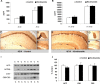
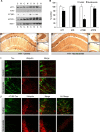
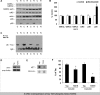
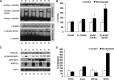
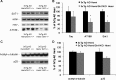
Memory loss is the signature feature of Alzheimer's disease, and therapies that prevent or delay its onset are urgently needed. Effective preventive strategies likely offer the greatest and most widespread benefits. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors increase histone acetylation and enhance memory and synaptic plasticity. We evaluated the efficacy of nicotinamide, a competitive inhibitor of the sirtuins or class III NAD(+)-dependent HDACs in 3xTg-AD mice, and found that it restored cognitive deficits associated with pathology. Nicotinamide selectively reduces a specific phospho-species of tau (Thr231) that is associated with microtubule depolymerization, in a manner similar to inhibition of SirT1. Nicotinamide also dramatically increased acetylated alpha-tubulin, a primary substrate of SirT2, and MAP2c, both of which are linked to increased microtubule stability. Reduced phosphoThr231-tau was related to a reduction of monoubiquitin-conjugated tau, suggesting that this posttranslationally modified form of tau may be rapidly degraded. Overexpression of a Thr231-phospho-mimic tau in vitro increased clearance and decreased accumulation of tau compared with wild-type tau. These preclinical findings suggest that oral nicotinamide may represent a safe treatment for AD and other tauopathies, and that phosphorylation of tau at Thr231 may regulate tau stability.
Figures
References
-
- Alonso AD, Grundke-Iqbal I, Barra HS, Iqbal K. Abnormal phosphorylation of tau and the mechanism of Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration: sequestration of microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 and the disassembly of microtubules by the abnormal tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:298–303. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angelo M, Plattner F, Irvine EE, Giese KP. Improved reversal learning and altered fear conditioning in transgenic mice with regionally restricted p25 expression. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18:423–431. - PubMed
-
- Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K, Pistell PJ, Poosala S, Becker KG, Boss O, Gwinn D, Wang M, Ramaswamy S, Fishbein KW, Spencer RG, Lakatta EG, et al. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature. 2006;444:337–342. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Billings LM, Oddo S, Green KN, McGaugh JL, LaFerla FM. Intraneuronal Abeta causes the onset of early Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive. 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
