Retinoic acid attenuates beta-amyloid deposition and rescues memory deficits in an Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse model
- PMID: 18987198
- PMCID: PMC3844785
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3153-08.2008
Retinoic acid attenuates beta-amyloid deposition and rescues memory deficits in an Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse model
Abstract
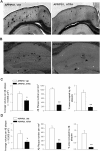
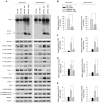
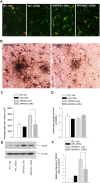
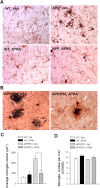
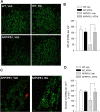
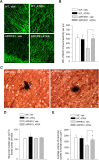
Recent studies have revealed that disruption of vitamin A signaling observed in Alzheimer's disease (AD) leads to beta-amyloid (Abeta) accumulation and memory deficits in rodents. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the therapeutic effect of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), an active metabolite of vitamin A, on the neuropathology and deficits of spatial learning and memory in amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin 1 (PS1) double-transgenic mice, a well established AD mouse model. Here we report a robust decrease in brain Abeta deposition and tau phosphorylation in the blinded study of APP/PS1 transgenic mice treated intraperitoneally for 8 weeks with ATRA (20 mg/kg, three times weekly, initiated when the mice were 5 months old). This was accompanied by a significant decrease in the APP phosphorylation and processing. The activity of cyclin-dependent kinase 5, a major kinase involved in both APP and tau phosphorylation, was markedly downregulated by ATRA treatment. The ATRA-treated APP/PS1 mice showed decreased activation of microglia and astrocytes, attenuated neuronal degeneration, and improved spatial learning and memory compared with the vehicle-treated APP/PS1 mice. These results support ATRA as an effective therapeutic agent for the prevention and treatment of AD.
Figures

References
-
- Anderton BH, Betts J, Blackstock WP, Brion JP, Chapman S, Connell J, Dayanandan R, Gallo JM, Gibb G, Hanger DP, Hutton M, Kardalinou E, Leroy K, Lovestone S, Mack T, Reynolds CH, Van Slegtenhorst M. Sites of phosphorylation in tau and factors affecting their regulation. Biochem Soc Symp. 2001;73 - PubMed
-
- Apelt J, Schliebs R. Beta-amyloid-induced glial expression of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in cerebral cortex of aged transgenic Tg2576 mice with Alzheimer plaque pathology. Brain Res. 2001;894:21–30. - PubMed
-
- Aplin AE, Gibb GM, Jacobsen JS, Gallo JM, Anderton BH. In vitro phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of the amyloid precursor protein by glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. J Neurochem. 1996;67:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Berse B, Blusztajn JK. Coordinated up-regulation of choline acetyltransferase and vesicular acetylcholine transporter gene expression by the retinoic acid receptor alpha, cAMP, and leukemia inhibitory factor/ciliary neurotrophic factor signaling pathways in a murine septal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:22101–22104. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard V, Moussaoui S, Czech C, Touchet N, Bonici B, Planche M, Canton T, Jedidi I, Gohin M, Wirths O, Bayer TA, Langui D, Duyckaerts C, Tremp G, Pradier L. Time sequence of maturation of dystrophic neurites associated with Abeta deposits in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Exp Neurol. 2003;184:247–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
