Structure of transmembrane pore induced by Bax-derived peptide: evidence for lipidic pores
- PMID: 18987313
- PMCID: PMC2582298
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0807764105
Structure of transmembrane pore induced by Bax-derived peptide: evidence for lipidic pores
Abstract
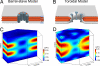
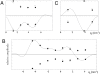
The structures of transmembrane pores formed by a large family of pore-forming proteins and peptides are unknown. These proteins, whose secondary structures are predominantly alpha-helical segments, and many peptides form pores in membranes without a crystallizable protein assembly, contrary to the family of beta-pore-forming proteins, which form crystallizable beta-barrel pores. Nevertheless, a protein-induced pore in membranes is commonly assumed to be a protein channel. Here, we show a type of peptide-induced pore that is not framed by a peptide structure. Peptide-induced pores in multiple bilayers were long-range correlated into a periodically ordered lattice and analyzed by X-ray diffraction. We found the pores induced by Bax-derived helical peptides were at least partially framed by a lipid monolayer. Evidence suggests that the formation of such lipidic pores is a major mechanism for alpha-pore-forming proteins, including apoptosis-regulator Bax.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Panchal RG, Smart ML, Bowser DN, Williams DA, Petrou S. Pore-forming proteins and their application in biotechnology. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2002;3:99–115. - PubMed
-
- Heuck AP, Tweten R K, Johnson AE. Beta-barrel pore-forming toxins: Intriguing dimorphic proteins. Biochemistry. 2001;40:9065–73. - PubMed
-
- Menestrina G, Serra MD, Lazarovici P. Pore-forming Peptides and Protein Toxins. London: Taylor & Francis; 2003. pp. 1–315.
-
- van der Goot FG. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Vol 257. Berlin: Springer; 2001. Pore-forming toxins; pp. 1–166.
-
- Zasloff M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature. 2002;415:389–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

