Varenicline for tobacco dependence
- PMID: 18987369
- PMCID: PMC2959114
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMct0800146
Varenicline for tobacco dependence
Abstract
A 57-year-old man with a 60-pack-year history visits his primary care provider because he wants to quit smoking. He has a history of stable coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, and hypertension. He also has severe obstructive lung disease (forced expiratory volume in 1 second, 39% of the predicted value) with a progressive increase in dyspnea. He has quit smoking and has had numerous relapses; the longest duration of abstinence from smoking was 7 months. Each relapse involved casual smoking to “test himself.” During previous attempts to quit, he has used a nicotine patch, a nicotine inhaler, and sustained-release bupropion. He feels motivated to quit smoking because he recently heard about a new medication to aid in quitting, and he wants to improve his health. The patient and his physician discuss the therapeutic options and agree that varenicline (Chantix) may be an option.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
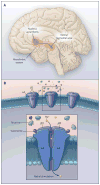
Comment in
-
Varenicline for tobacco dependence.N Engl J Med. 2009 Feb 12;360(7):730-1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc082464. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19213691 No abstract available.
-
Varenicline for tobacco dependence.N Engl J Med. 2009 Feb 12;360(7):731. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19222131 No abstract available.
References
-
- Prevalence of current cigarette smoking among adults and changes in prevalence of current and some day smoking — United States, 1996–2001. JAMA. 2003;289:2355–6. - PubMed
-
- Mokdad AH, Marks JS, Stroup DF, Gerberding JL. Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. JAMA. 2004;291:1238–45. [Errata, JAMA 2005;293:293–4, 298.] - PubMed
-
- Annual smoking-attributable mortality, years of potential life lost, and economic costs — United States, 1995–1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002;51:300–3. - PubMed
-
- Department of Health and Human Services. The health consequences of smoking: a report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta: National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; 2004.
-
- Cigarette smoking among adults — United States, 2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007;56:1157–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
