A miRNA signature of prion induced neurodegeneration
- PMID: 18987751
- PMCID: PMC2575400
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003652
A miRNA signature of prion induced neurodegeneration
Abstract
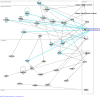
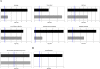
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules which are emerging as key regulators of numerous cellular processes. Compelling evidence links miRNAs to the control of neuronal development and differentiation, however, little is known about their role in neurodegeneration. We used microarrays and RT-PCR to profile miRNA expression changes in the brains of mice infected with mouse-adapted scrapie. We determined 15 miRNAs were de-regulated during the disease processes; miR-342-3p, miR-320, let-7b, miR-328, miR-128, miR-139-5p and miR-146a were over 2.5 fold up-regulated and miR-338-3p and miR-337-3p over 2.5 fold down-regulated. Only one of these miRNAs, miR-128, has previously been shown to be de-regulated in neurodegenerative disease. De-regulation of a unique subset of miRNAs suggests a conserved, disease-specific pattern of differentially expressed miRNAs is associated with prion-induced neurodegeneration. Computational analysis predicted numerous potential gene targets of these miRNAs, including 119 genes previously determined to be also de-regulated in mouse scrapie. We used a co-ordinated approach to integrate miRNA and mRNA profiling, bioinformatic predictions and biochemical validation to determine miRNA regulated processes and genes potentially involved in disease progression. In particular, a correlation between miRNA expression and putative gene targets involved in intracellular protein-degradation pathways and signaling pathways related to cell death, synapse function and neurogenesis was identified.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
CDKN2A, NF2, and JUN are dysregulated among other genes by miRNAs in malignant mesothelioma -A miRNA microarray analysis.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009 Jul;48(7):615-23. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20669. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19396864
-
Target identification of microRNAs expressed highly in human embryonic stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Apr 15;106(6):1020-30. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22084. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19229866
-
Development of a micro-array to detect human and mouse microRNAs and characterization of expression in human organs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Dec 22;32(22):e188. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh186. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15616155 Free PMC article.
-
Function of microRNA-375 and microRNA-124a in pancreas and brain.FEBS J. 2009 Nov;276(22):6509-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07353.x. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 20102393 Review.
-
miR-21 as a key regulator of oncogenic processes.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Aug;37(Pt 4):918-25. doi: 10.1042/BST0370918. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19614619 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic silencing of miR-338-3p contributes to tumorigenicity in gastric cancer by targeting SSX2IP.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 24;8(6):e66782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066782. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826132 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNA Let-7 in Modulating Multifactorial Aspect of Neurodegenerative Diseases: an Overview.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):2787-2793. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9145-y. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25823513 Review.
-
MicroRNA 433 regulates nonsense-mediated mRNA decay by targeting SMG5 mRNA.BMC Mol Biol. 2016 Jul 29;17(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12867-016-0070-z. BMC Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27473591 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of post-transcriptional gene regulatory networks associated with autism spectrum disorders by microRNA expression profiling of lymphoblastoid cell lines.Genome Med. 2010 Apr 7;2(4):23. doi: 10.1186/gm144. Genome Med. 2010. PMID: 20374639 Free PMC article.
-
A Complex Network of MicroRNAs Expressed in Brain and Genes Associated with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Int J Genomics. 2013;2013:383024. doi: 10.1155/2013/383024. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Int J Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23936767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Booth S, Bowman C, Baumgartner R, Sorensen G, Robertson C, et al. Identification of central nervous system genes involved in the host response to the scrapie agent during preclinical and clinical infection. J Gen Virol. 2004;85(Pt 11):3459–3471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

