S-glutathionylation impairs signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and signaling
- PMID: 18988672
- PMCID: PMC2654735
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2008-1241
S-glutathionylation impairs signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and signaling
Abstract
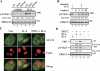
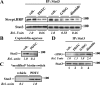
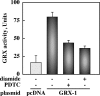
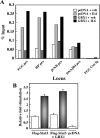
S-glutathionylation is a physiological, reversible protein modification of cysteine residues with glutathione in response to mild oxidative stress. Because the key cell growth regulator signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 is particularly susceptible to redox regulation, we hypothesized that oxidative modification of cysteine residues of STAT3 by S-glutathionylation may occur. Herein, we show that the cysteine residues of STAT3 are modified by a thiol-alkylating agent and are the targets of S-glutathionylation. STAT3 protein thiol reactivity was reversibly attenuated with concomitant increase in the S-glutathionylation of STAT3 upon treatment of human HepG2 hepatoma cells with pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, glutathione disulfide, or diamide. Under these conditions there was a marked reduction in IL-6-dependent STAT3 signaling, including decreased STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation, loss in nuclear accumulation of STAT3, and impaired expression of target genes, such as fibrinogen-gamma. In a cell-free system, diamide induced glutathionylation of STAT3, which was decreased upon addition of glutaredoxin (GRX)-1, a deglutathionylation enzyme, or the reducing agent, dithiothreitol. Glutathionylated STAT3 was a poor Janus protein tyrosine kinase 2 substrate in vitro, and it exhibited low DNA-binding activity. Cellular GRX-1 activity was inhibited by diamide and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate treatment; however, ectopic expression of GRX-1 was accompanied by a modest increase in phosphorylation, nuclear translocation, and DNA-binding ability of STAT3 in response to IL-6. These results are the first to show S-glutathionylation of STAT3, a modification that may exert regulatory function in STAT3 signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Kishimoto T 2005 Interleukin-6: from basic science to medicine—40 years in immunology. Annu Rev Immunol 23:1–21 - PubMed
-
- Schuringa JJ, Schepers H, Vellenga E, Kruijer W 2001 Ser727-dependent transcriptional activation by association of p300 with STAT3 upon IL-6 stimulation. FEBS Lett 495:71–76 - PubMed
-
- Kortylewski M, Feld F, Krüger KD, Bahrenberg G, Roth RA, Joost HG, Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Barthel A 2003 Akt modulates STAT3-mediated gene expression through a FKHR (FOXO1a)-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 278:5242–5249 - PubMed
-
- Lufei C, Koh TH, Uchida T, Cao X 2007 Pin1 is required for the Ser727 phosphorylation-dependent Stat3 activity. Oncogene 26:7656–7664 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

