Effective visualization of complex vascular structures using a non-parametric vessel detection method
- PMID: 18989016
- PMCID: PMC2636705
- DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2008.123
Effective visualization of complex vascular structures using a non-parametric vessel detection method
Abstract
The effective visualization of vascular structures is critical for diagnosis, surgical planning as well as treatment evaluation. In recent work, we have developed an algorithm for vessel detection that examines the intensity profile around each voxel in an angiographic image and determines the likelihood that any given voxel belongs to a vessel; we term this the "vesselness coefficient" of the voxel. Our results show that our algorithm works particularly well for visualizing branch points in vessels. Compared to standard Hessian based techniques, which are fine-tuned to identify long cylindrical structures, our technique identifies branches and connections with other vessels. Using our computed vesselness coefficient, we explore a set of techniques for visualizing vasculature. Visualizing vessels is particularly challenging because not only is their position in space important for clinicians but it is also important to be able to resolve their spatial relationship. We applied visualization techniques that provide shape cues as well as depth cues to allow the viewer to differentiate between vessels that are closer from those that are farther. We use our computed vesselness coefficient to effectively visualize vasculature in both clinical neurovascular x-ray computed tomography based angiography images, as well as images from three different animal studies. We conducted a formal user evaluation of our visualization techniques with the help of radiologists, surgeons, and other expert users. Results indicate that experts preferred distance color blending and tone shading for conveying depth over standard visualization techniques.
Figures



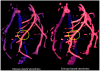
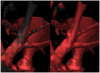
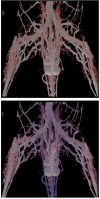

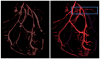



References
-
- Bruckner S, Gröller ME. Enhancing depth-perception with flexible volumetric halos. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics. 2007 Oct;13(6):1344–1351. - PubMed
-
- Bühler K, Felkel P, Cruz AL. Geometric methods for vessel visualization and quantification- a survey. In: Brunnett HMG, Hamann B, editors. Geometric Modelling for Scientific Visualization. 2003. Springer
-
- Chen CW, Huang TS. Epicardial motion and deformation estimation from coronary artery bifurcation points; Proc. Int. Conf. on Computer Vision; 1990.Dec., pp. 456–459.
-
- Cover TM, Thomas JA. Elements of Information Theory. Wiley; 1991.
-
- Frangi AF, Niessen WJ, Vincken KL, Viergever MA. Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering. Proc. of MICCAI, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 1998;1496:130–137.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

