The role of p44/42 activation in tributyltin-induced inhibition of human natural killer cells: effects of MEK inhibitors
- PMID: 18989867
- PMCID: PMC2642538
- DOI: 10.1002/jat.1397
The role of p44/42 activation in tributyltin-induced inhibition of human natural killer cells: effects of MEK inhibitors
Abstract
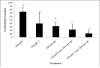
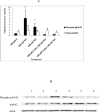
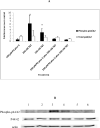
Destruction of tumor cells is a key function of natural killer (NK) cells. Previous studies have shown that tributyltin (TBT) can significantly reduce the lytic function of the human NK cells with accompanying increases in the phosphorylation (activation) states of the mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs), p44/42. The current studies examine the role of p44/42 activation in the TBT-induced reduction of NK-lytic function, by using MAPK kinase (MEK) inhibitors, PD98059 and U0126. A 1 h treatment with PD98059 or U0126 or both decreased the ability of NK cells to lyse K562 tumor cells. PD98059, U0126 or a combination of both inhibitors were able to completely block TBT-induced activation of p44/42. However, when p44/42 activation was blocked by the presence of PD98059, U0126 or the combination, subsequent exposure to TBT was still able to decrease the lytic function of NK cells. These results indicate that TBT-induced activation of p44/42 occurs via the activation of its upstream activator, MEK, and not by a TBT-induced inhibition of p44/42 phosphatase activity. Additionally, as lytic function was never completely blocked by MEK inhibitors, the results indicate that activation of p44/42 pathway is not solely responsible for the activation of lytic function of freshly isolated human NK cells. Finally, the results showed that TBT-induced activation of p44/42 is not solely responsible for the loss of lytic function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of p44/42 MAPK plays a role in the TBT-induced loss of human natural killer (NK) cell function.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2010 Oct;26(5):435-44. doi: 10.1007/s10565-010-9154-6. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20213532 Free PMC article.
-
Tributyltin-induced effects on MAP kinases p38 and p44/42 in human natural killer cells.Toxicology. 2005 May 5;209(3):263-77. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2004.12.034. Toxicology. 2005. PMID: 15795062
-
Alteration of an essential NK cell signaling pathway by low doses of tributyltin in human natural killer cells.Toxicology. 2006 Jul 25;224(3):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.05.002. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Toxicology. 2006. PMID: 16781040
-
Activation of p44/42 in human natural killer cells decreases cell-surface protein expression: Relationship to tributyltin-induced alterations of protein expression.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2010 Nov;20(9):544-55. doi: 10.3109/15376516.2010.518174. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2010. PMID: 20883105 Free PMC article.
-
The ups and downs of structure-activity landscapes.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;672:101-17. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-839-3_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20838965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of p44/42 MAPK plays a role in the TBT-induced loss of human natural killer (NK) cell function.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2010 Oct;26(5):435-44. doi: 10.1007/s10565-010-9154-6. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20213532 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protein kinase C in TBT-induced inhibition of lytic function and MAPK activation in human natural killer cells.Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2010 Nov;59(4):661-9. doi: 10.1007/s00244-010-9520-7. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20390410 Free PMC article.
-
Tributyltin alters secretion of interleukin 1 beta from human immune cells.J Appl Toxicol. 2015 Aug;35(8):895-908. doi: 10.1002/jat.3087. Epub 2014 Nov 7. J Appl Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25382723 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative global phosphoproteomics analysis of obinutuzumab (GA101) versus rituximab (RTX) against RTX sensitive and resistant Burkitt lymphoma (BL) demonstrates differential phosphorylation of signaling pathway proteins after treatment.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 9;8(69):113895-113909. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23040. eCollection 2017 Dec 26. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29371955 Free PMC article.
-
Ziram activates mitogen-activated protein kinases and decreases cytolytic protein levels in human natural killer cells.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2011 Oct;21(8):577-84. doi: 10.3109/15376516.2011.578170. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2011. PMID: 21859362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aluoch AO, Odman-Ghazi SO, Whalen MM. Alteration of an essential NK cell signaling pathway by low doses of tributyltin in human natural killer cells. Toxicology. 2006;224:229–237. - PubMed
-
- Aluoch AO, Whalen MM. Tributyltin-induced effects on MAP kinases p38 and p44/42 in human natural killer cells. Toxicology. 2005;209:263–277. - PubMed
-
- Baaijens PA. Health effect screening and biological monitoring for workers in organotin industries.. Toxicology analytics of the tributyltins: the present F status, Proceedings of the ORTEPA Workshop Berlin; ORTEP-Association, Vlissingen-Oost, The Netherlands. 15−16 May.1986. pp. 191–208.
-
- Camps M, Nichols A, Arkinstall S. Dual Specificity phosphatases: a gene family for control of MAP kinase functions. FASEB J. 2000;14:6–16. - PubMed
-
- Chan G, Hanks T, Fisher KD. Vav-1 regulates NK T cell development and NK cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001;31:2403–2410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

