Standing after spinal cord injury with four-contact nerve-cuff electrodes for quadriceps stimulation
- PMID: 18990650
- PMCID: PMC2936226
- DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2008.2003390
Standing after spinal cord injury with four-contact nerve-cuff electrodes for quadriceps stimulation
Abstract
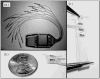
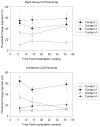
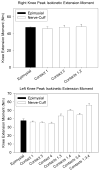
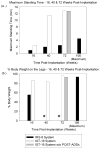
This paper describes the performance of a 16-channel implanted neuroprosthesis for standing and transfers after spinal cord injury including four-contact nerve-cuff electrodes stimulating the femoral nerve for knee extension. Responses of the nerve-cuffs were stable and standing times increased by 600% over time-matched values with a similar eight-channel neuroprosthesis utilizing muscle-based electrodes on vastus lateralis for knee extension.
Figures
References
-
- Jaeger R, Yarkony G, Smith R. Standing the spinal cord injured patient by electrical stimulation: Refinement of a protocol for clinical use. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1989;36:720–728. - PubMed
-
- Kralj A, Bajd T. Functional Electrical Stimulation: Standing and Walking After Spinal Cord Injury. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1989.
-
- Davis JA, Triolo RJ, Uhlir JP, Bieri C, Rohde L, Lissy D. Preliminary Performance of a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis for standing and transfers – Where do we stand? J Rehabil Res Dev. 2001;38(6):609–617. - PubMed
-
- Davis JA, Triolo RJ, Uhlir JP, Bhadra N, Lissy DA, Nandurkar S, Marsolais EB. Surgical technique for installing an 8-channel neuroprosthesis for standing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;4:237–252. - PubMed
-
- Triolo RJ, Bieri C, Uhlir J, Kobetic R, Scheiner A, Marsolais EB. Implanted FNS systems for assisted standing and transfers for individuals with cervical spinal cord injuries: clinical case reports. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996;77(11):1119–1128. - PubMed

