A novel signaling pathway impact analysis
- PMID: 18990722
- PMCID: PMC2732297
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn577
A novel signaling pathway impact analysis
Abstract
Motivation: Gene expression class comparison studies may identify hundreds or thousands of genes as differentially expressed (DE) between sample groups. Gaining biological insight from the result of such experiments can be approached, for instance, by identifying the signaling pathways impacted by the observed changes. Most of the existing pathway analysis methods focus on either the number of DE genes observed in a given pathway (enrichment analysis methods), or on the correlation between the pathway genes and the class of the samples (functional class scoring methods). Both approaches treat the pathways as simple sets of genes, disregarding the complex gene interactions that these pathways are built to describe.
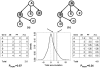
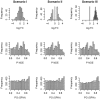
Results: We describe a novel signaling pathway impact analysis (SPIA) that combines the evidence obtained from the classical enrichment analysis with a novel type of evidence, which measures the actual perturbation on a given pathway under a given condition. A bootstrap procedure is used to assess the significance of the observed total pathway perturbation. Using simulations we show that the evidence derived from perturbations is independent of the pathway enrichment evidence. This allows us to calculate a global pathway significance P-value, which combines the enrichment and perturbation P-values. We illustrate the capabilities of the novel method on four real datasets. The results obtained on these data show that SPIA has better specificity and more sensitivity than several widely used pathway analysis methods.
Availability: SPIA was implemented as an R package available at http://vortex.cs.wayne.edu/ontoexpress/
Figures


References
-
- Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001;29:1165–1188.
-
- Bethin KE, et al. Microarray analysis of uterine gene expression in mouse and human pregnancy. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003;17:1454–1469. - PubMed
-
- Breuiller-Fouche M, Germain G. Gene and protein expression in the myometrium in pregnancy and labor. Reproduction. 2006;131:837–850. - PubMed
-
- Drăghici S. Statistical intelligence: effective analysis of high-density microarray data. Drug Discov. Today. 2002;7:S55–S63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

