Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor imaging and therapy
- PMID: 18990940
- PMCID: PMC2626938
- DOI: 10.2147/ijn.s2824
Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor imaging and therapy
Abstract
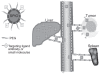
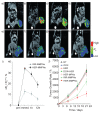
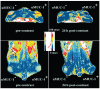
Magnetic iron oxide (IO) nanoparticles with a long blood retention time, biodegradability and low toxicity have emerged as one of the primary nanomaterials for biomedical applications in vitro and in vivo. IO nanoparticles have a large surface area and can be engineered to provide a large number of functional groups for cross-linking to tumor-targeting ligands such as monoclonal antibodies, peptides, or small molecules for diagnostic imaging or delivery of therapeutic agents. IO nanoparticles possess unique paramagnetic properties, which generate significant susceptibility effects resulting in strong T2 and T*2 contrast, as well as T1 effects at very low concentrations for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is widely used for clinical oncology imaging. We review recent advances in the development of targeted IO nanoparticles for tumor imaging and therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Artemov D, Mori N, Okollie B, et al. MR molecular imaging of theHer-2/neu receptor in breast cancer cells using targeted iron oxide nanoparticles. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49:403–8. - PubMed
-
- Aslam M, Fu L, Li S, et al. Silica encapsulation and magnetic properties of FePt nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;290:444–9. - PubMed
-
- Atri M. New technologies and directed agents for applications of cancer imaging. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3299–308. - PubMed
-
- Bae Y, Diezi TA, Zhao A, et al. Mixed polymeric micelles for combination cancer chemotherapy through the concurrent delivery of multiple chemotherapeutic agents. J Control Release. 2007;122:324–30. - PubMed
-
- Berry CC, Wells S, Charles S, et al. Cell response to dextran-derivatised iron oxide nanoparticles post internalisation. Biomaterials. 2004;25:5405–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

