Synergistic effect of the combination of nanoparticulate Fe3O4 and Au with daunomycin on K562/A02 cells
- PMID: 18990943
- PMCID: PMC2626936
Synergistic effect of the combination of nanoparticulate Fe3O4 and Au with daunomycin on K562/A02 cells
Abstract
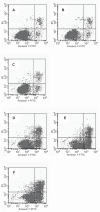
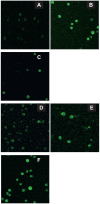
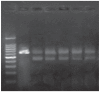
In this study, we have explored the possibility of the combination of the high reactivity of nano Fe3O4 or Au nanoparticles and daunomycin, one of the most important antitumor drugs in the treatment of acute leukemia clinically, to inhibit MDR of K562/A02 cells. Initially, to determine whether the magnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4 and Au can facilitate the anticancer drug to reverse the resistance of cancer cells, we have explored the cytotoxic effect of daunomycin (DNR) with and without the magnetic nano-Fe3O4 or nano-Au on K562 and K562/A02 cells by MTT assay. Besides, the intracellular DNR concentration and apoptosis of the K562/A02 cells was further investigated by flow cytometry and confocal fluorescence microscopic studies. The MDR1 gene expression of the K562/A02 cells was also studied by RT-PCR method. Our results indicate that 5.0 x 10(-7) M nano-Fe3O4 or 2.0 x 10(-8) M nano-Au is biocompatible and can apparently raise the intracellular DNR accumulation of the K562/A02 cells and increase the apoptosis of tumor cells. Moreover, our observations illustrate that although these two kinds of nanoparticles themselves could not lower the MDRI gene expression of the K562/A02 cells, yet they could degrade the MDR1 gene level when combining with anticancer drug DNR. This raises the possibility to combine the nano-Fe3O4 or nano-Au with DNR to reverse the drug resistance of K562/A02 cells, which could offer a new strategy for the promising efficient chemotherapy of the leukemia patients.
Figures


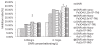
Similar articles
-
Effect of magnetic nanoparticles of Fe3O4 and 5-bromotetrandrine on reversal of multidrug resistance in K562/A02 leukemic cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2009;4:209-16. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s7090. Epub 2009 Oct 19. Int J Nanomedicine. 2009. PMID: 19918367 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic mechanism of human leukemia K562/A02 cells induced by magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles co-loaded with daunorubicin and 5-bromotetrandrin.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:1027-34. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S18023. Epub 2011 May 17. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011. PMID: 21720514 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of multidrug resistance by magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle copolymerizating daunorubicin and MDR1 shRNA expression vector in leukemia cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2010 Aug 9;5:437-44. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s10083. Int J Nanomedicine. 2010. PMID: 20957165 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of multidrug resistance by magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle copolymerizating daunorubicin and 5-bromotetrandrine in xenograft nude-mice.Int J Nanomedicine. 2009;4:73-8. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s5093. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Int J Nanomedicine. 2009. PMID: 19421372 Free PMC article.
-
[The study on reversing mechanism of multidrug resistance of K562/A02 cell line by curcumin and erythromycin].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Apr;27(4):254-8. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16875558 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Increased Uptake of Silica Nanoparticles in Inflamed Macrophages but Not upon Co-Exposure to Micron-Sized Particles.Cells. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):2099. doi: 10.3390/cells9092099. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32942641 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect of magnetic nanoparticles of Fe(3)O(4) with gambogic acid on apoptosis of K562 leukemia cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2009;4:251-9. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s7932. Int J Nanomedicine. 2009. PMID: 20011242 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding nanoparticle endocytosis to improve targeting strategies in nanomedicine.Chem Soc Rev. 2021 May 7;50(9):5397-5434. doi: 10.1039/d0cs01127d. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Chem Soc Rev. 2021. PMID: 33666625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive cytotoxicity studies of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018 Jan 8;13:63-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.12.002. eCollection 2018 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018. PMID: 29349357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered nanoparticles induce cell apoptosis: potential for cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):40882-40903. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8553. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27056889 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Advani R, Saba HI, Tallman MS, et al. Treatment of refractory and relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia with combination chemotherapy plus the multidrug resistance modulator PSC 833 (Valspodar) Blood. 1999;93:787–95. - PubMed
-
- Lamprecht A, Benoit JP. Etoposide nanocarriers suppress glioma cell growth by intracellular drug delivery and simultaneous P-glycoprotein inhibition. J Control Release. 2006;112:208–13. - PubMed
-
- Bennis S, Chapey C, Couvreur P, et al. Enhanced cytotoxicity of doxorubicin encapsulated in polyisohexylcyanoacrylate nanospheres against multidrug-resistant tumour cells in culture. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A:89–93. - PubMed
-
- Bradley G, Juranka PF, Ling V. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1999;948:87–128. - PubMed
-
- Brigger I, Dubernet C, Couvreur P. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Drug Delivery. 2002;54:631–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

