Identifying targets for COPD treatment through gene expression analyses
- PMID: 18990963
- PMCID: PMC2629979
- DOI: 10.2147/copd.s1758
Identifying targets for COPD treatment through gene expression analyses
Abstract
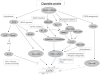
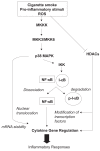
Despite the status of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) as a major global health problem, no currently available therapies can limit COPD progression. Therefore, an urgent need exists for the development of new and effective treatments for COPD. An improved understanding in the molecular pathogenesis of COPD can potentially identify molecular targets to facilitate the development of new therapeutic modalities. Among the best approaches for understanding the molecular basis of COPD include gene expression profiling techniques, such as serial analysis of gene expression or microarrays. Using these methods, recent studies have mapped comparative gene expression profiles of lung tissues from patients with different stages of COPD relative to healthy smokers or non-smokers. Such studies have revealed a number of differentially-regulated genes associated with COPD progression, which include genes involved in the regulation of inflammation, extracellular matrix, cytokines, chemokines, apoptosis, and stress responses. These studies have shed new light on the molecular mechanisms of COPD, and suggest novel targets for clinical treatments.
Figures
References
-
- Akhurst RJ. Large- and small-molecule inhibitors of transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;7:513–21. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Adcock IM, Ito K. Histone acetylation and deacetylation: importance in inflammatory lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 2005;25:552–63. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Hansel TT. Prospects for new drugs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2004;364:985–96. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Shapiro SD, Pauwels RA. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: molecular and cellular mechanisms. Eur Respir J. 2003;22:672–88. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ. Novel approaches and targets for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:S72–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

