Imaging of EGFR and EGFR tyrosine kinase overexpression in tumors by nuclear medicine modalities
- PMID: 18991714
- PMCID: PMC2778093
- DOI: 10.2174/138161208786404326
Imaging of EGFR and EGFR tyrosine kinase overexpression in tumors by nuclear medicine modalities
Abstract
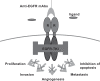
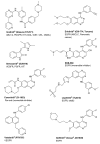
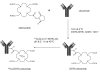
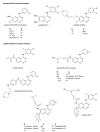
Protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) play a pivotal role in signal transduction pathways and in the development and maintenance of various cancers. They are involved in multiple processes such as transcription, cell cycle progression, proliferation, angiogenesis and inhibition of apoptosis. Among the PTKs, the EGFR is one of the most widely studied and has emerged as a promising key target for the treatment of cancer. Indeed, several drugs directed at this receptor are FDA-approved and many others are at various stages of development. However, thus far, the therapeutic outcome of EGFR-targeted therapy is suboptimal and needs to be refined. Quantitative PET molecular imaging coupled with selective labelled biomarkers may facilitate in vivo EGFR-targeted drug efficacy by noninvasively assessing the expression of EGFR in tumor, guiding dose and regime by measuring target drug binding and receptor occupancy as well as potentially detecting the existence of a primary or secondary mutation leading to either drug interaction or failure of EGFR recognition by the drug. This review describes the attempts to develop labelled EGFR molecular imaging agents that are based either on low molecular weight tyrosine kinase inhibitors or monoclonal antibodies directed to the extracellular binding domain of the receptor to be used in nuclear medicine modalities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Some implications of receptor kinase signaling pathway for development of multitargeted kinase inhibitors.Curr Radiopharm. 2013 Mar;6(1):48-55. doi: 10.2174/1874471011306010008. Curr Radiopharm. 2013. PMID: 23278847 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Jun;15(2):420-34. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8229-y. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23575987 Review.
-
Strategies for molecular imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase in cancer.J Nucl Med. 2009 Aug;50(8):1199-202. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.062117. Epub 2009 Jul 17. J Nucl Med. 2009. PMID: 19617320 Review.
-
Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor in solid tumors: critical evaluation of the biological importance of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(29):3797-804. doi: 10.2174/092986709789177984. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19747140 Review.
-
Receptor-binding, biodistribution, and metabolism studies of 64Cu-DOTA-cetuximab, a PET-imaging agent for epidermal growth-factor receptor-positive tumors.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2008 Apr;23(2):158-71. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2007.0444. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2008. PMID: 18454685
Cited by
-
Molecular imaging in clinical trials.Target Oncol. 2009 Sep;4(3):151-68. doi: 10.1007/s11523-009-0117-x. Epub 2009 Sep 21. Target Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19768637 Review.
-
The role of EGFR/PI3K/Akt/cyclinD1 signaling pathway in acquired middle ear cholesteatoma.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:651207. doi: 10.1155/2013/651207. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 24311896 Free PMC article.
-
Interrogating tumor metabolism and tumor microenvironments using molecular positron emission tomography imaging. Theranostic approaches to improve therapeutics.Pharmacol Rev. 2013 Sep 24;65(4):1214-56. doi: 10.1124/pr.113.007625. Print 2013. Pharmacol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24064460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of 64Cu-radiolabeled NOTA-cetuximab (64Cu-NOTA-C225) for immuno-PET imaging of EGFR expression.Chin J Cancer Res. 2019 Apr;31(2):400-409. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.02.14. Chin J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31156310 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis by Dual-probe Optical Imaging.Theranostics. 2017 Jan 1;7(1):153-163. doi: 10.7150/thno.17085. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 28042324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2002;55:75–108. - PubMed
-
- Ciardiello F. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors as agents. Drugs. 2000;60:25–32. - PubMed
-
- Renhowe PA. Growth factor receptor kinases in cancer. Ann Rep Med Chem. 2001;36:109–18.
-
- Rowinsky EK. The pursuit of optimal outcomes in cancer therapy in a new age of rationally designed target-based anticancer agents. Drugs. 2000;1:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
