Molecular genetics of addiction and related heritable phenotypes: genome-wide association approaches identify "connectivity constellation" and drug target genes with pleiotropic effects
- PMID: 18991966
- PMCID: PMC3922196
- DOI: 10.1196/annals.1441.018
Molecular genetics of addiction and related heritable phenotypes: genome-wide association approaches identify "connectivity constellation" and drug target genes with pleiotropic effects
Abstract
Genome-wide association (GWA) can elucidate molecular genetic bases for human individual differences in complex phenotypes that include vulnerability to addiction. Here, we review (a) evidence that supports polygenic models with (at least) modest heterogeneity for the genetic architectures of addiction and several related phenotypes; (b) technical and ethical aspects of importance for understanding GWA data, including genotyping in individual samples versus DNA pools, analytic approaches, power estimation, and ethical issues in genotyping individuals with illegal behaviors; (c) the samples and the data that shape our current understanding of the molecular genetics of individual differences in vulnerability to substance dependence and related phenotypes; (d) overlaps between GWA data sets for dependence on different substances; and (e) overlaps between GWA data for addictions versus other heritable, brain-based phenotypes that include bipolar disorder, cognitive ability, frontal lobe brain volume, the ability to successfully quit smoking, neuroticism, and Alzheimer's disease. These convergent results identify potential targets for drugs that might modify addictions and play roles in these other phenotypes. They add to evidence that individual differences in the quality and quantity of brain connections make pleiotropic contributions to individual differences in vulnerability to addictions and to related brain disorders and phenotypes. A "connectivity constellation" of brain phenotypes and disorders appears to receive substantial pathogenic contributions from individual differences in a constellation of genes whose variants provide individual differences in the specification of brain connectivities during development and in adulthood. Heritable brain differences that underlie addiction vulnerability thus lie squarely in the midst of the repertoire of heritable brain differences that underlie vulnerability to other common brain disorders and phenotypes.
Figures
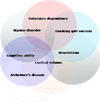
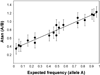
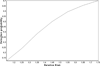
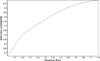
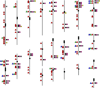
References
-
- Coon KD, et al. A high-density whole-genome association study reveals that APOE is the major susceptibility gene for sporadic late-onset Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(4):613–618. - PubMed
-
- Li H, et al. Candidate Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms From a Genomewide Association Study of Alzheimer Disease. Arch Neurol. 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL051429/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DA000401/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA63562/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DA000401/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- DA08511/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DA014276/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 1K08 DA14276-05/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DA000492/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA000492/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P50 CA084719/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL51429/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL32318/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA84719/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DA000537/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HD13138/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DA000165/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063562/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA/DA84718/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

