The effect of methyl sulphonyl methane supplementation on biomarkers of oxidative stress in sport horses following jumping exercise
- PMID: 18992134
- PMCID: PMC2586020
- DOI: 10.1186/1751-0147-50-45
The effect of methyl sulphonyl methane supplementation on biomarkers of oxidative stress in sport horses following jumping exercise
Abstract
Background: Exercise induces changes in several organs and tissues, and this process might be due to oxidative damage caused by free radicals and inflammatory mediators. Methyl Sulphonyl Methane, better known as MSM, is a naturally occurring sulphur compound with well-known antioxidant properties. On the other hand, Vitamin C is important in limiting free radical damage in the aqueous phase of the cell, and cellular vitamin C status may be linked to the mechanisms involved in quenching cellular reactive oxygen species. The aim of this study was to determine if supplementation with MSM and vitamin C could alleviate exercise-induced oxidative stress in horses undergoing jumping competition.
Methods: Twenty four jumping horses involved in competition were used. Horses were given the following three treatment diets: control (without supplementation), MSM 8 mg/kg, and combined supplements (MSM 8 mg/kg + Vit-C 5 mg/kg). EDTA blood samples were collected before exercise, upon arrived to the schooling area (control), and each week after last show. Nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, lipid hydroperoxides and the antioxidant enzymes, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione transferase and glutathione reductase, plasma levels were determined.
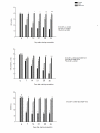
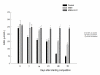
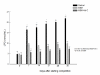
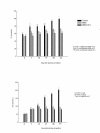
Results: Competition induced a significant increase in lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide and carbon monoxide. By contrary, reduced glutathione as well as antioxidant enzyme activities, were decreased. MSM administration significantly ameliorated all these exercise-related changes, and this effect was potentiated by Vit C reaching values in some of the parameters similar to those found before competition.
Conclusion: These results suggest that jumping exercise could induce harmful effects on horses, probably due to an increase in oxidative damage and proinflammatory molecules. In addition, we have demonstrated that MSM could exert some protective effect on oxidative and inflammatory exercise-induced injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of oxidative stress during exercise in the horse.J Anim Sci. 2016 Oct;94(10):4067-4075. doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-9988. J Anim Sci. 2016. PMID: 27898872
-
Antioxidant supplementation and pulmonary function at rest and exercise.Equine Vet J Suppl. 2002 Sep;(34):58-65. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.2002.tb05392.x. Equine Vet J Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12405660
-
Moderate exercise with a dietary vitamin C and E combination protects against streptozotocin-induced oxidative damage to the blood and improves fetal outcomes in pregnant rats.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2004 May;42(5):511-7. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2004.087. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2004. PMID: 15202787
-
Methylsulfonylmethane: Applications and Safety of a Novel Dietary Supplement.Nutrients. 2017 Mar 16;9(3):290. doi: 10.3390/nu9030290. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28300758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Sport Horses: Potential Biomarkers and Modulators of Exercise Adaptation and Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 3;26(9):4359. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094359. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of methylsulfonylmethane on growth performance, immunity, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality in Pekin ducks.Poult Sci. 2020 Feb;99(2):1069-1074. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.10.002. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32029143 Free PMC article.
-
PCL and DMSO2 Composites for Bio-Scaffold Materials.Materials (Basel). 2023 Mar 21;16(6):2481. doi: 10.3390/ma16062481. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984361 Free PMC article.
-
The preventive effects of two nutraceuticals on experimentally induced acute synovitis.Equine Vet J. 2017 Jul;49(4):532-538. doi: 10.1111/evj.12629. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Equine Vet J. 2017. PMID: 27554764 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of single dose administration of methylsulfonylmethane on oxidative stress following acute exhaustive exercise.Iran J Pharm Res. 2013 Fall;12(4):845-53. Iran J Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 24523764 Free PMC article.
-
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) Supplementation in Adult Horses Supports Improved Skeletal Muscle Inflammatory Gene Expression Following Exercise.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;15(2):215. doi: 10.3390/ani15020215. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson MJPS, Bolaños J, Bruckdorfer R, Carlssen H, Elliot RM, Flier J, Griffiths HR, Heales S, Holst B, Lorusso M, Lund E, Moskaug JO, Moser U, Di Paola M, Polidori MC, Signorile A, Stahl W, Viña-Ribes J, Astley SB. Antioxidants, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, gene induction and mitochondrial function. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. 2002;23:209–285. doi: 10.1016/S0098-2997(02)00018-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

