Exploring valid reference genes for gene expression studies in Brachypodium distachyon by real-time PCR
- PMID: 18992143
- PMCID: PMC2588586
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-8-112
Exploring valid reference genes for gene expression studies in Brachypodium distachyon by real-time PCR
Abstract
Background: The wild grass species Brachypodium distachyon (Brachypodium hereafter) is emerging as a new model system for grass crop genomics research and biofuel grass biology. A draft nuclear genome sequence is expected to be publicly available in the near future; an explosion of gene expression studies will undoubtedly follow. Therefore, stable reference genes are necessary to normalize the gene expression data.
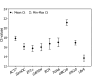
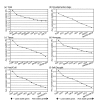
Results: A systematic exploration of suitable reference genes in Brachypodium is presented here. Nine reference gene candidates were chosen, and their gene sequences were obtained from the Brachypodium expressed sequence tag (EST) databases. Their expression levels were examined by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) using 21 different Brachypodium plant samples, including those from different plant tissues and grown under various growth conditions. Effects of plant growth hormones were also visualized in the assays. The expression stability of the candidate genes was evaluated using two analysis software packages, geNorm and NormFinder. In conclusion, the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 18 gene (UBC18) was validated as a suitable reference gene across all the plant samples examined. While the expression of the polyubiquitin genes (Ubi4 and Ubi10) was most stable in different plant tissues and growth hormone-treated plant samples, the expression of the S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase gene (SamDC) ranked was most stable in plants grown under various environmental stresses.
Conclusion: This study identified the reference genes that are most suitable for normalizing the gene expression data in Brachypodium. These reference genes will be particularly useful when stress-responsive genes are analyzed in order to produce transgenic plants that exhibit enhanced stress resistance.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

