Hepatocyte growth factor enhances death receptor-induced apoptosis by up-regulating DR5
- PMID: 18992144
- PMCID: PMC2590617
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-325
Hepatocyte growth factor enhances death receptor-induced apoptosis by up-regulating DR5
Abstract
Background: Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor c-MET are commonly expressed in malignant gliomas and embryonic neuroectodermal tumors including medulloblastoma and appear to play an important role in the growth and dissemination of these malignancies. Dependent on cell context and the involvement of specific downstream effectors, both pro- and anti-apoptotic effects of HGF have been reported.
Methods: Human medulloblastoma cells were treated with HGF for 24-72 hours followed by death receptor ligand TRAIL (Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) for 24 hours. Cell death was measured by MTT and Annexin-V/PI flow cytometric analysis. Changes in expression levels of targets of interest were measured by Northern blot analysis, quantitative reverse transcription-PCR, Western blot analysis as well as immunoprecipitation.
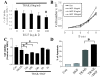
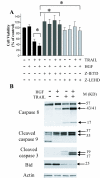
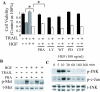
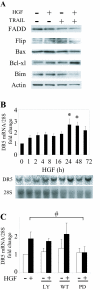
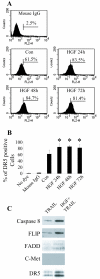
Results: In this study, we show that HGF promotes medulloblastoma cell death induced by TRAIL. TRAIL alone triggered apoptosis in DAOY cells and death was enhanced by pre-treating the cells with HGF for 24-72 h prior to the addition of TRAIL. HGF (100 ng/ml) enhanced TRAIL (10 ng/ml) induced cell death by 36% (P<0.001). No cell death was associated with HGF alone. Treating cells with PHA-665752, a specific c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, significantly abrogated the enhancement of TRAIL-induced cell death by HGF, indicating that its death promoting effect requires activation of its canonical receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell death induced by TRAIL+HGF was predominately apoptotic involving both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways as evidenced by the increased activation of caspase-3, 8, 9. Promotion of apoptosis by HGF occurred via the increased expression of the death receptor DR5 and enhanced formation of death-inducing signal complexes (DISC).
Conclusion: Taken together, these and previous findings indicate that HGF:c-Met pathway either promotes or inhibits medulloblastoma cell death via pathway and context specific mechanisms.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

