Acyclic nucleoside bisphosphonates: synthesis and properties of chiral 2-amino-4,6-bis[(phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]pyrimidines
- PMID: 18992968
- PMCID: PMC2706328
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.09.031
Acyclic nucleoside bisphosphonates: synthesis and properties of chiral 2-amino-4,6-bis[(phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]pyrimidines
Abstract
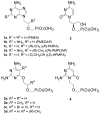
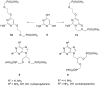
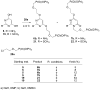
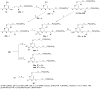
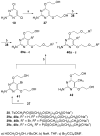
2-Amino-4,6-bis[(phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]pyrimidines bearing two equal or different achiral or chiral phosphonoalkoxy chains have been prepared either by aromatic nucleophilic substitution of 2-amino-4,6-dichloropyrimidine or by alkylation of 4,6-dihydroxy-2-(methylsulfanyl)pyrimidine with appropriate phosphonate-bearing building block. Alkylation of 4,6-dihydroxy-2-(methylsulfanyl)pyrimidine proved to be the method of choice for efficient preparation of variety of bisphosphonates. The enantiomeric purity of selected compounds was determined by capillary electrophoresis. Antiviral activity of bisphosphonates is discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
6-[2-(Phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]pyrimidines with antiviral activity.J Med Chem. 2002 Apr 25;45(9):1918-29. doi: 10.1021/jm011095y. J Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 11960502
-
5-Substituted-2,4-diamino-6-[2-(phosphonomethoxy)ethoxy]pyrimidines-acyclic nucleoside phosphonate analogues with antiviral activity.J Med Chem. 2003 Nov 6;46(23):5064-73. doi: 10.1021/jm030932o. J Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14584956
-
The unsaturated acyclic nucleoside analogues bearing a sterically constrained (Z)-4'-benzamido-2'-butenyl moiety: Synthesis, X-ray crystal structure study, cytostatic and antiviral activity evaluations.Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Sep 1;18(17):6249-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.07.035. Epub 2010 Aug 7. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20696582
-
6-[2-phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]-2,4-diaminopyrimidines: a new class of acyclic pyrimidine nucleoside phosphonates with antiviral activity.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2004 Oct;23(8-9):1321-7. doi: 10.1081/NCN-200027573. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2004. PMID: 15571252
-
The synthesis and antiviral properties of acyclic nucleoside analogues with a phosphonomethoxy fragment in the side chain.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(24):2953-80. doi: 10.2174/092986706778521896. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 17073640 Review.
Cited by
-
An improved synthesis of adefovir and related analogues.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2019 Mar 29;15:801-810. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.15.77. eCollection 2019. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2019. PMID: 30992729 Free PMC article.
-
Acyclic nucleoside thiophosphonates as potent inhibitors of HIV and HBV replication.Eur J Med Chem. 2011 Sep;46(9):4281-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.06.034. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21803462 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the reactivity of (9-Methyl-5,6-dihydronaphtho[1â,2â:4,5]-thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-11-yl)hydrazine towards some reagents for biological evaluation.Sci Pharm. 2010 Jan-Mar;78(1):1-12. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.0910-11. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Sci Pharm. 2010. PMID: 21179366 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of N-substituted 5-iodouracils as antimicrobial and anticancer agents.Molecules. 2009 Jul 27;14(8):2768-79. doi: 10.3390/molecules14082768. Molecules. 2009. PMID: 19701123 Free PMC article.
-
Design, evaluation, cytotoxic activity, molecular docking, ADMET analysis, and dynamic simulations and the preparation of new isoxazoles, thiazoles, 1,3-thiazines, and thiazolopyrimidines derived from quinoline-pyridopyrimidines.Pharm Biol. 2025 Dec;63(1):607-644. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2025.2547744. Epub 2025 Aug 19. Pharm Biol. 2025. PMID: 40827848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naesens L, Snoeck R, Andrei G, Balzarini J, Neyts J, De Clercq E. Antivir Chem Chemother. 1997;8:1–23.
- Ying C, De Clercq E, Neyts J. J Viral Hepat. 2000;7:79–83. - PubMed
-
- Starrett JE, Jr, Tortolani DR, Hitchcock MJ, Martin JC, Mansuri MM. Antiviral Res. 1992;19:267–273. - PubMed
-
- Tsai CC, Follis KE, Beck TW, Sabo A, Bischofberger N, Dailey PJ. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1997;13:707–712. - PubMed
- Srinivas RV, Fridland A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:1484–1487. - PMC - PubMed
- Suruga Y, Makino M, Okada Y, Tanaka H, De Clercq E, Baba M. J Acquired Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1998;18:316–322. - PubMed
- Van Rompay KK, Miller MD, Marthas ML, Margot NA, Dailey PJ, Canfield DR, Tarara PR, Cherrington JM, Aguirre NL, Bischofberger N, Pedersen NC. J Virol. 2000;74:1767–1774. - PMC - PubMed
- Grim SA, Romanelli F. Annals of Pharmacother. 2003;37:849–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

