Novel actions of estrogen to promote proliferation: integration of cytoplasmic and nuclear pathways
- PMID: 18996136
- PMCID: PMC2702758
- DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2008.10.014
Novel actions of estrogen to promote proliferation: integration of cytoplasmic and nuclear pathways
Abstract
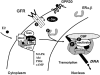
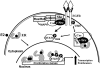
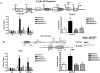
Both steroids and growth factors stimulate proliferation of steroid-dependent tumor cells, and interaction between these signaling pathways occurs at several levels. Steroid receptors are classified as ligand-activated transcription factors, and steps by which they activate target gene transcription are well understood. Several steroid responses have now been functionally linked to other intracellular signaling pathways, including c-Src or tyrosine kinase receptors. Steroids such as 17beta-estradiol (E2), via binding to cytoplasmic or membrane-associated receptors, were also shown to rapidly activate intracellular signaling cascades such as ERK, PI3K and STATs. These E2-stimulated phosphorylations can then contribute to altered tumor cell function. ER-positive breast cancer cells, in which proliferation is stimulated by E2 and suppressed by antiestrogens, have been of particular interest in dissecting nuclear and cytoplasmic roles of estrogen receptors (ER). In some cell contexts, ER interacts directly with the intracellular tyrosine kinase c-Src and other cytoplasmic signaling and adaptor molecules, such as Shc, PI3K, MNAR, and p130 Cas. Although the hierarchy among these associations is not known, it is clear that c-Src plays a fundamental role in both growth factor and E2-stimulated cell growth, and this may also require other growth factor receptors such as those for EGF or IGF-1. STAT transcription factors represent one pathway to integrate E2 cytoplasmic and nuclear signaling. STAT5 is phosphorylated in the cytoplasm at an activating tyrosine in response to E2 or EGF, and then is translocated to the nucleus to stimulate target gene transcription. E2 stimulates recruitment of STAT5 and ER to the promoter of several proliferative genes, and STAT5 knockdown prevents recruitment of either protein to these promoters. STAT5 activation by E2 in breast cancer cells requires c-Src and EGF receptor, and inhibition of c-Src or EGFR, or knockdown of STAT5, prevents E2 stimulation of several genes and breast cancer cell proliferation. Hyperactivation of the growth factor receptor-c-Src pathway can in some contexts decrease growth responses to E2, or render cells and tumors resistant to suppressive actions of endocrine therapies. Crosstalk between growth factors and steroids in both the cytoplasm and nucleus may thus have a profound impact on complex biological processes such as cell growth, and may play a significant role in the treatment of steroid-dependent breast cancers.
Figures
References
-
- Nilsson S, Makela S, Treuter E, Tujague M, Thomsen J, Andersson G, et al. Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:1535–65. - PubMed
-
- Parsons SJ, Parsons JT. Src family kinases, key regulators of signal transduction. Oncogene. 2004;18(23):7906–9. - PubMed
-
- Shupnik MA. Crosstalk between steroid receptors and the c-Src-receptor tyrosine kinase pathways: implications for cell proliferation. Oncogene. 2004;23:7979–89. - PubMed
-
- Levin ER. Bidirectional signaling between the estrogen receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:309–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

