Ov-APR-1, an aspartic protease from the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini: functional expression, immunolocalization and subsite specificity
- PMID: 18996218
- PMCID: PMC2683748
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.10.013
Ov-APR-1, an aspartic protease from the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini: functional expression, immunolocalization and subsite specificity
Abstract
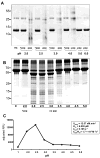
The human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini is endemic in Thailand, Laos and Cambodia where long standing infection is associated with cancer of the bile ducts, cholangiocarcinoma. Here we describe a cathepsin D-like aspartic protease from the gut and other tissues in O. viverrini. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that Ov-APR-1 is cathepsin D-like, conforming with Clan AA, Family A1 of the MEROPS classification. Ov-APR-1 is expressed in the gut of the mature hermaphroditic parasite, in the reproductive tissues including the testis and immature spermatids, and the developing miracidium within the eggshell. The enzyme was also detected in the excretory/secretory products of cultured adult flukes, indicating a role in host-parasite relationships. A recombinant form of the enzyme expressed in Escherichia coli and refolded from denatured inclusion bodies underwent autocatalytic activation and demonstrated hydrolytic activity against the peptide substrate 7-methoxycoumarin-4-acetyl-GKPILFFRLK(DNP)-D-Arg-amide with a k(cat)/K(m)=1.7 x 10(4)M(-1)s(-1) and a pH optimum around pH 2.5-3.0. The recombinant enzyme digested hemoglobin and bovine serum albumin. Forty-six serum albumin peptides were detected after digestion with recombinant Ov-APR-1 and sequenced. Like many other aspartic proteases, Ov-APR-1 displayed promiscuous preferences for residues accommodated at the key subsites of the binding pocket although hydrophobic (Leu, Ala, Ile), positively charged (Lys) and bulky aromatic (Phe) residues, in that order, were preferred at P1. Similar residues were accommodated at P1' although even less selectivity was exerted at this position.
Figures

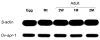


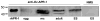


Similar articles
-
Cathepsin F cysteine protease of the human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;3(3):e398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000398. Epub 2009 Mar 24. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009. PMID: 19308250 Free PMC article.
-
Asparaginyl endopeptidase from the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, and its potential for serodiagnosis.Int J Infect Dis. 2008 Nov;12(6):e49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2008.03.033. Epub 2008 Jul 10. Int J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18619888 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular expression and enzymatic characterization of thioredoxin from the carcinogenic human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini.Parasitol Int. 2012 Mar;61(1):101-6. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2011.06.018. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Parasitol Int. 2012. PMID: 21740981 Free PMC article.
-
Current assessment of the systematics and population genetics of Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato (Trematoda: Opisthorchiidae) and its first intermediate host Bithynia siamensis sensu lato (Gastropoda: Bithyniidae) in Thailand and Southeast Asia.Infect Genet Evol. 2022 Jan;97:105182. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105182. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Infect Genet Evol. 2022. PMID: 34902557 Review.
-
Infection with the carcinogenic human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini.Mol Biosyst. 2011 May;7(5):1367-75. doi: 10.1039/c0mb00295j. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Mol Biosyst. 2011. PMID: 21311794 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Surface molecules of extracellular vesicles secreted by the helminth pathogen Fasciola hepatica direct their internalisation by host cells.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jan 18;13(1):e0007087. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007087. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30657764 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of a Trichinella spiralis aspartic protease and its facilitation role in larval invasion of host intestinal epithelial cells.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Apr 27;14(4):e0008269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008269. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32339171 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genes and proteins of Clonorchis sinensis.Korean J Parasitol. 2009 Oct;47 Suppl(Suppl):S59-68. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2009.47.S.S59. Korean J Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19885336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial Characterization of Two Cathepsin D Family Aspartic Peptidases of Clonorchis sinensis.Korean J Parasitol. 2019 Dec;57(6):671-680. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2019.57.6.671. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Korean J Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31914521 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel Opisthorchis viverrini calcium-binding EF-hand protein.Parasitol Int. 2012 Mar;61(1):94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Parasitol Int. 2012. PMID: 21782972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcala-Canto Y, Ibarra-Velarde F, Sumano-Lopez H, Gracia-Mora J, Alberti-Navarro A. Effect of a cysteine protease inhibitor on Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke) fecundity, egg viability, parasite burden, and size in experimentally infected sheep. Parasitol Res. 2007;100:461–5. - PubMed
-
- Becker MM, Harrop SA, Dalton JP, Kalinna BH, McManus DP, Brindley PJ. Cloning and characterization of the Schistosoma japonicum aspartic proteinase involved in hemoglobin degradation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:24496–501. - PubMed
-
- Brindley PJ, Kalinna BH, Wong JY, Bogitsh BJ, King LT, Smyth DJ, et al. Proteolysis of human hemoglobin by schistosome cathepsin D. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001;112:103–12. - PubMed
-
- Caffrey CR, McKerrow JH, Salter JP, Sajid M. Blood ‘n’ guts: an update on schistosome digestive peptidases. Trends Parasitol. 2004;20:241–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

