Critical role of PBEF expression in pulmonary cell inflammation and permeability
- PMID: 18996492
- PMCID: PMC3732657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2008.10.015
Critical role of PBEF expression in pulmonary cell inflammation and permeability
Abstract
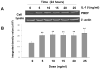
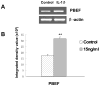
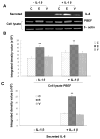
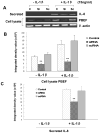
Previous studies in our lab have identified pre-B-cell colony enhancing factor (PBEF) as a novel biomarker in acute lung injury. This study continues to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism of PBEF in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury in pulmonary cell culture models. Our results revealed that IL-1beta induced PBEF expression in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells at the transcriptional level and a -1535 T-variant in the human PBEF gene promoter significantly attenuated its binding to an IL-1beta-induced unknown transcription factor. This may underlie the reduced expression of PBEF and thus the lower susceptibility to acute lung injury in -1535T carriers. Furthermore, overexpression of PBEF significantly augmented IL-8 secretion and mRNA expression by more than 6-fold and 2-fold in A549 cells and HPAEC, respectively. It also significantly augmented IL-1beta-mediated cell permeability by 44% in A549 cells and 65% in endothelial cells. The knockdown of PBEF expression significantly inhibited IL-1beta-stimulated IL-8 secretion and mRNA level by 60% and 70%, respectively, and the knockdown of PBEF expression also significantly attenuated IL-1beta-induced cell permeability by 29% in epithelial cells and 24% in endothelial cells. PBEF expression also affected the expression of two other inflammatory cytokines (IL-16 and CCR3 genes). These results suggest that PBEF is critically involved in pulmonary vascular and epithelial inflammation and permeability, which are hallmark features in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. This study lends further support to our finding that PBEF is a potential new target in acute lung injury.
Figures







References
-
- Adams JM, Hauser CJ, Livingston DH, Lavery RF, Fekete Z, Deitch EA. Early trauma polymorphonuclear neutrophil responses to chemokines are associated with development of sepsis, pneumonia, and organ failure. J Trauma. 2001;51:452–456. - PubMed
-
- Bachofen M, Weibel ER. Alterations of the gas exchange apparatus in adult respiratory insufficiency associated with septicemia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977;116:589–615. - PubMed
-
- Bachofen M, Weibel ER. Structural alterations of lung parenchyma in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Chest Med. 1982;3:35–56. - PubMed
-
- Bajwa EK, Yu C, Gong MN, Thompson BT, Christiani DC. PBEF gene polymorphisms influence the risk of developing ARDS. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;3:A272.
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72(7):248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

