Trans fatty acids: effects on cardiometabolic health and implications for policy
- PMID: 18996687
- PMCID: PMC2639783
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plefa.2008.09.008
Trans fatty acids: effects on cardiometabolic health and implications for policy
Abstract
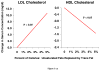
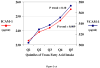
In both developed and developing countries, trans fatty acids (TFA) are largely consumed from partially hydrogenated vegetable oils. This article focuses on TFA as a modifiable dietary risk factor for cardiovascular disease, reviewing the evidence for lipid and non-lipid effects; the relations of trans fat intake with clinical endpoints; and current policy and legislative issues. In both observational cohort studies and randomized clinical trials, TFA adversely affect lipid profiles (including raising LDL and triglyceride levels, and reducing HDL levels), systemic inflammation, and endothelial function. More limited but growing evidence suggests that TFA also exacerbate visceral adiposity and insulin resistance. These potent effects of TFA on a multitude of cardiovascular risk factors are consistent with the strong associations seen in prospective cohort studies between TFA consumption and risk of myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease (CHD) death. The documented harmful effects of TFA along with the feasibility of substituting partially hydrogenated vegetable oils with healthy alternatives indicate little reason for continued presence of industrially produced TFA in food preparation and manufacturing or in home cooking fats/oils. A comprehensive strategy to eliminate the use of industrial TFA in both developed and developing countries, including education, food labeling, and policy and legislative initiatives, would likely prevent tens of thousands of CHD events worldwide each year.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- American Heart Association. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics - 2004 Update. [Acessed 4/28/2004, 2004]. pp. 25–26. www.americanheart.org.
-
- Mozaffarian D, et al. Dietary fish and omega-3 fatty acid consumption and heart rate variability in US adults. Circulation. 2008;117(9):1130–7. - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D. Effects of dietary fats versus carbohydrates on coronary heart disease: A review of the evidence. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2005;7(6):435–445. - PubMed
-
- Allison DB, et al. Estimated intakes of trans fatty and other fatty acids in the US population. J Am Diet Assoc. 1999;99(2):166–74. - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D, et al. Consumption of trans fats and estimated effects on coronary heart disease in Iran. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007;61:1004–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

