Simultaneous absence of surfactant proteins A and D increases lung inflammation and injury after allogeneic HSCT in mice
- PMID: 18996902
- PMCID: PMC2643990
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90253.2008
Simultaneous absence of surfactant proteins A and D increases lung inflammation and injury after allogeneic HSCT in mice
Abstract
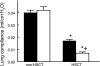
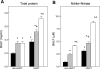
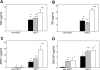
The relative contributions of the hydrophilic surfactant proteins (SP)-A and -D to early inflammatory responses associated with lung dysfunction after experimental allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) were investigated. We hypothesized that the absence of SP-A and SP-D would exaggerate allogeneic T cell-dependent inflammation and exacerbate lung injury. Wild-type, SP-D-deficient (SP-D(-/-)), and SP-A and -D double knockout (SP-A/D(-/-)) C57BL/6 mice were lethally conditioned with cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation and given allogeneic bone marrow plus donor spleen T cells, simulating clinical HSCT regimens. On day 7, after HSCT, permeability edema progressively increased in SP-D(-/-) and SP-A/D(-/-) mice. Allogeneic T cell-dependent inflammatory responses were also increased in SP-D(-/-) and SP-A/D(-/-) mice, but the altered mediators of inflammation were not identical. Compared with wild-type, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) levels of nitrite plus nitrate, GM-CSF, and MCP-1, but not TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma, were higher in SP-D-deficient mice before and after HSCT. In SP-A/D(-/-) mice, day 7 post-HSCT BALF levels of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma, in addition to nitrite plus nitrate and MCP-1, were higher compared with mice lacking SP-D alone. After HSCT, both SP-A and SP-D exhibited anti-inflammatory lung-protective functions that were not completely redundant in vivo.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Surfactant protein A decreases lung injury and mortality after murine marrow transplantation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002 Sep;27(3):297-305. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2002-0035OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12204891
-
Surfactant protein A is a required mediator of keratinocyte growth factor after experimental marrow transplantation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003 Sep;285(3):L602-10. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00088.2003. Epub 2003 May 9. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12740217
-
Human surfactant protein a suppresses T cell-dependent inflammation and attenuates the manifestations of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome in mice.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001 May;24(5):527-36. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.24.5.4400. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11350821
-
Surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D as modulators of the allergic inflammation in asthma.Pathobiology. 2002-2003;70(5):287-92. doi: 10.1159/000070744. Pathobiology. 2002. PMID: 12771511 Review.
-
Surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D in human health and disease.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2005 Sep-Oct;53(5):399-417. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2005. PMID: 16314824 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel role for surfactant protein A in gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease.J Immunol. 2012 May 15;188(10):4897-905. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103558. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22508928 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of irradiation/bone marrow transplantation on alveolar epithelial type II cells is aggravated in surfactant protein D deficient mice.Histochem Cell Biol. 2017 Jan;147(1):49-61. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1479-7. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27565967
-
Surfactant Protein D in Respiratory and Non-Respiratory Diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Feb 8;5:18. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00018. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29473039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immunity of surfactant proteins A and D in urinary tract infection with uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Innate Immun. 2016 Jan;22(1):9-20. doi: 10.1177/1753425915609973. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Innate Immun. 2016. PMID: 26511057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atochina EN, Beers MF, Hawgood S, Poulain F, Davis C, Fusaro T, Gow AJ. Surfactant protein-D, a mediator of innate lung immunity, alters the products of nitric oxide metabolism. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 30: 271–279, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Atochina EN, Gow AJ, Beck JM, Haczku A, Inch A, Kadire H, Tomer Y, Davis C, Preston AM, Poulain F, Hawgood S, Beers MF. Delayed clearance of pneumocystis carinii infection, increased inflammation, and altered nitric oxide metabolism in lungs of surfactant protein-D knockout mice. J Infect Dis 189: 1528–1539, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Borron PJ, Mostaghel EA, Doyle C, Walsh ES, Heyzer-Williams MG, Wright JR. Pulmonary surfactant proteins A and D directly suppress CD3+/CD4+ cell function: evidence for two shared mechanisms. J Immunol 169: 5844–5850, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

