NT-proBNP and the diagnosis of exercise-induced myocardial ischaemia
- PMID: 18997988
- PMCID: PMC3971619
NT-proBNP and the diagnosis of exercise-induced myocardial ischaemia
Abstract
Background: Amino terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is a sensitive marker of ventricular dysfunction. Exercise causes an increase in the secretion of NTproBNP, and with myocardial ischaemia the increase is more pronounced. This increase has been found to improve the diagnostic sensitivity of the stress ECG in diagnosing myocardial ischaemia in subjects with normal ventricular function.
Objective: To assess whether the change in NT-proBNP can be used to diagnose effort-induced myocardial ischaemia in an unselected population.
Methods: We enrolled a total of 51 consecutive patients, referred for exercise stress 99mTc-sestamibi SPECT MPI (single-photon emission computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging) to diagnose inducible myocardial ischaemia. NT-proBNP was determined at rest and 30 minutes after cessation of exercise.
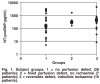
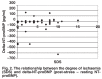
Results: Of the 51 patients, 28 had normal perfusion scans, seven had scans with fixed perfusion defects (previous myocardial infarction with no inducible ischaemia) and 16 had reversible perfusion defects (inducible ischaemia). There was no correlation between ischaemia and resting NT-proBNP, post-stress NT-proBNP or the change in NTproBNP (delta-NT-proBNP).
Conclusion: In an unselected population the change in NTproBNP cannot be used to diagnose effort-induced myocardial ischaemia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Does dipyridamole-induced ischaemia affect NT-proBNP secretion?Cardiovasc J Afr. 2007 Nov-Dec;18(6):371-4. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2007. PMID: 18092112 Free PMC article.
-
Use of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide to detect myocardial ischemia.Am J Med. 2005 Nov;118(11):1287. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.05.020. Am J Med. 2005. PMID: 16271916
-
[N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and ischemia modified albumin (IMA) in exercise induced ischemia in patients with stable coronary artery disease].Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2006 Jul;116(1):640-7. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2006. PMID: 17340970 Polish.
-
Can exercise-induced changes in B-type natriuretic peptides be used to detect cardiac ischemia?J Card Fail. 2005 Jun;11(5 Suppl):S59-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2005.04.021. J Card Fail. 2005. PMID: 15948103 Review.
-
Evaluation of TMT abnormalities in asymptomatic persons using myocardial perfusion study.J Assoc Physicians India. 2011 Mar;59:155-6, 161-3. J Assoc Physicians India. 2011. PMID: 21751624 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of prealbumin, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, heart type fatty acid binding protein, and cardiac troponin I in elderly patients for heart failure and poor outcomes.J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):300060521999742. doi: 10.1177/0300060521999742. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34039072 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid upregulation and clearance of distinct circulating microRNAs after prolonged aerobic exercise.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014 Mar 1;116(5):522-31. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01141.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 16. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014. PMID: 24436293 Free PMC article.
-
Serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, amyloid associated protein and N-terminal proBNP levels do not predict reversible myocardial ischaemia.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2011 Mar-Apr;22(2):85-9. doi: 10.5830/cvja-2010-041. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2011. PMID: 21556451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costello-Boerrigter LC, Burnett JC (jun). The prognostic value of N-terminal proB-type natriuretic peptide. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc. 2005;2:194–201. - PubMed
-
- Anand IS, Fisher LD, Chiang Y, Latini R, Masson S, Maggioni AP. et al. Changes in brain natriuretic peptide and norepinephrine over time and mortality and morbidity in the Valsaratan Heart Failure Trial (Val-HeFT). Circulation. 2003;107:1278–1283. - PubMed
-
- Schnabel R, Lubos E, Rupprecht H, Espinola-Klein C, Bickel C, Lackner KJ. et al. B-type natriuretic peptide and the risk of cardiovascular events and death in patients with stable angina. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:552–558. - PubMed
-
- Pegoraro NR, Naidoo DP, Esterhuizen TM. Prognostic value of Nterminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide measurement in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Cardiovasc J S Afr. 2006;17:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Morrow DA, De Lemos JA, Blazing MA, Sabatine MC, Murphy SA, Jarolim P. et al. Prognostic value of serial B-type natriuretic peptide testing during follow-up of patients with unstable coronary artery disease. J Am Med Assoc. 2005;294:2866–2871. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

