Frequent deletion of ING2 locus at 4q35.1 associates with advanced tumor stage in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 18998165
- PMCID: PMC12160168
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-008-0507-y
Frequent deletion of ING2 locus at 4q35.1 associates with advanced tumor stage in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in the ING family members has been shown in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) except for ING2. Like all the other members of ING family, ING2, which is located at chromosome 4q35.1, is a promising tumor suppressor gene (TSG). In this study, we performed LOH analysis of ING2 in HNSCC and compared it with clinicopathological variables.
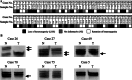
Materials and methods: We performed LOH analysis in DNAs from 80 paired of normal and HNSCC tissues, using a specifically designed microsatellite marker on chromosome 4q35.1, which detects allelic loss of ING2. TP53 mutation analysis and its relationship with ING2 chromosomal deletion were also performed in available 68 of the samples. The correlation between LOH status and clinicopathological characteristics was evaluated by using statistical methods. The overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS) were also determined.
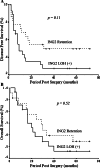
Results: LOH was detected in 54.6% (30/55) of the informative samples. Statistical significance was obtained between LOH and tumor (T) stage (P = 0.02), application of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Positive node status (N) appeared to be the only independent prognostic factor for both OS (P = 0.031) and DFS (P = 0.044).
Conclusions: Our study showed allelic loss of 4q35.1 in HNSCC. The high percentage of LOH suggests ING2 as a candidate TSG in HNSCC. High LOH frequency was statistically associated with advanced T stage, suggesting that ING2 LOH might occur in late stages during HNSCC progression.
Figures

References
-
- Baker SJ, Fearon ER, Nigro JM, Hamilton SR, Preisinger AC, Jessup JM, van Tuinen P, Ledbetter DH, Barker DF, Nakamura Y, White R, Vogelstein B (1989) Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science 244(4901):217–221. doi:10.1126/science.2649981 - PubMed
-
- Beder LB, Gunduz M, Ouchida M, Gunduz E, Sakai A, Fukushima K, Nagatsuka H, Ito S, Honjo N, Nishizaki K, Shimizu K (2006) Identification of a candidate tumor suppressor gene RHOBTB1 located at a novel allelic loss region 10q21 in head and neck cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132(1):19–27. doi:10.1007/s00432-005-0033-0 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bradford CR, Zhu S, Poore J, Fisher SG, Beals TF, Thoraval D, Hanash SM, Carey TE, Wolf GT (1997) p53 mutation as a prognostic marker in advanced laryngeal carcinoma. Department of Veterans Affairs Laryngeal Cancer Cooperative Study Group. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123(6):605–609 - PubMed
-
- Cabelguenne A, Blons H, de Waziers I, Carnot F, Houllier AM, Soussi T, Brasnu D, Beaune P, Laccourreye O, Laurent-Puig P (2000) p53 alterations predict tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a prospective series. J Clin Oncol 18(7):1465–1473 - PubMed
-
- Cengiz B, Gunduz M, Nagatsuka H, Beder L, Gunduz E, Tamamura R, Mahmut N, Fukushima K, Ali MA, Naomoto Y, Shimizu K, Nagai N (2007) Fine deletion mapping of chromosome 2q21-37 shows three preferentially deleted regions in oral cancer. Oral Oncol 43(3):241–247. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2006.03.004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

