Early depletion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific T helper 1 cell responses after HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 19000013
- PMCID: PMC2650495
- DOI: 10.1086/593017
Early depletion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific T helper 1 cell responses after HIV-1 infection
Abstract
Background: The acid-fast bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis is often the first manifestation of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This study was conducted to better understand the mechanism underlying M. tuberculosis-specific pathogenicity early after onset of HIV infection.
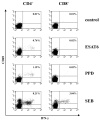
Methods: M. tuberculosis-specific T helper 1 (Th1) cells were studied in HIV negative (n=114) and chronically HIV infected (n=68) Tanzanian subjects by using early secreted antigenic target 6 (ESAT6) protein or tuberculin (purified protein derivative) with interferon-gamma ELISPOT and intracellular cytokine staining. In a longitudinal study, the effect of acute HIV infection on M. tuberculosis-specific Th1 cells was determined by polychromatic flow cytometric analysis in 5 subjects with latent M. tuberculosis infection who became infected with HIV.
Results: In tuberculosis (TB)-asymptomatic subjects (i.e., subjects with unknown TB status who did not show clinical signs suggestive of TB), chronic HIV infection was associated with a decreased percentage of subjects with detectable M. tuberculosis-specific Th1 cells (P< .001) a decrease which was not observed among subjects with active TB. Acute HIV infection induced a rapid depletion of M. tuberculosis-specific Th1 cells in 4 subjects remained TB asymptomatic, whereas the population of these cells remained stable in subjects who remained HIV negative (P< .01).
Conclusions: Taken together, these data suggest a mechanism of rapid M. tuberculosis-specific Th1 cell depletion that may contribute to the early onset of TB in individuals with latent M. tuberculosis infection who become HIV infected.
Figures



Comment in
-
Significance of early secreted antigenic target 6-specific T cell depletion after HIV-1 infection.J Infect Dis. 2009 Jul 1;200(1):158; author reply 158-9. doi: 10.1086/599362. J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19485778 No abstract available.
References
-
- Li Q, Duan L, Estes JD, et al. Peak SIV replication in resting memory CD4+ T cells depletes gut lamina propria CD4+ T cells. Nature. 2005;434:1148–52. - PubMed
-
- Mattapallil JJ, Douek DC, Hill B, Nishimura Y, Martin M, Roederer M. Massive infection and loss of memory CD4+ T cells in multiple tissues during acute SIV infection. Nature. 2005;434:1093–7. - PubMed
-
- Grossman Z, Meier-Schellersheim M, Paul WE, Picker LJ. Pathogenesis of HIV infection: what the virus spares is as important as what it destroys. Nat Med. 2006;12:289–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

