Agreement of the order of overall performance levels under different reading paradigms
- PMID: 19000873
- PMCID: PMC2601626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2008.07.011
Agreement of the order of overall performance levels under different reading paradigms
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: To investigate consistency of the orders of performance levels when interpreting mammograms under three different reading paradigms.
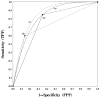
Materials and methods: We performed a retrospective observer study in which nine experienced radiologists rated an enriched set of mammography examinations that they personally had read in the clinic ("individualized") mixed with a set that none of them had read in the clinic ("common set"). Examinations were interpreted under three different reading paradigms: binary using screening Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS), receiver-operating characteristic (ROC), and free-response ROC (FROC). The performance in discriminating between cancer and noncancer findings under each of the paradigms was summarized using Youden's index/2+0.5 (Binary), nonparameteric area under the ROC curve (AUC), and an overall FROC index (JAFROC-2). Pearson correlation coefficients were then computed to assess consistency in the ordering of observers' performance levels. Statistical significance of the computed correlation coefficients was assessed using bootstrap confidence intervals obtained by resampling sets of examination-specific observations.
Results: All but one of the computed pair-wise correlation coefficients were larger than 0.66 and were significantly different from zero. The correlation between the overall performance measures under the Binary and ROC paradigms was the lowest (0.43) and was not significantly different from zero (95% confidence interval -0.078 to 0.733).
Conclusion: The use of different evaluation paradigms in the laboratory tends to lead to consistent ordering of the overall performance levels of observers. However, one should recognize that conceptually similar performance indexes resulting from different paradigms often measure different performance characteristics and thus disagreements are not only possible but frequently quite natural.
Figures
References
-
- DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the area under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845. - PubMed
-
- Dorfman DD, Berbaum KS, Metz CE. Receiver operating characteristic rating analysis. Generalization to the population of readers and patients with the jackknife method. Invest Radiol. 1992;27(9):723–731. - PubMed
-
- Obuchowski NA, Rockette HE. Hypothesis testing of the diagnostic accuracy for multiple diagnostic tests: an ANOVA approach with dependent observations. Communications Statistics Simulations Computations. 1995;24:285–308.
-
- Beiden SV, Wagner RF, Campbell G. Components of variance models and multiple bootstrap experiments: An alternative method for random effects, receiver operating characteristics analysis. Acad Radiol. 2000;7:341–349. - PubMed
-
- Ishwaran H, Gatsonis CA. A general class of hierarchical ordinal regression models with applications to correlated ROC analysis. The Canadian Journal of Statistics. 2000;28:731–750.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

