Acute regulation of metabolic genes and insulin receptor substrates in the liver of mice by one single bout of treadmill exercise
- PMID: 19001047
- PMCID: PMC2670037
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.160275
Acute regulation of metabolic genes and insulin receptor substrates in the liver of mice by one single bout of treadmill exercise
Abstract
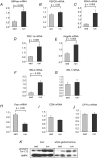
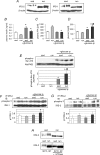
Acute exercise performance represents a major metabolic challenge for the skeletal muscle, but also for the liver as the most important source of energy. However the molecular adaptation of the liver to one single bout of exercise is largely unknown. C57BL/6 mice performed a 60 min treadmill run at high aerobic intensity. Liver, soleus and white gastrocnemius muscle were removed immediately after exercise. The single bout of exercise resulted in a very rapid and pronounced induction of hepatic metabolic enzymes and regulators of metabolism or transcription: glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase; 3-fold), pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-4 (PDK4; 4.8-fold), angiopoietin-like 4 (2.1-fold), insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-2 (5.1-fold), peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha; 3-fold). In soleus and white gastrocnemius muscle the up-regulation of IRS-2 and PDK4 was less pronounced compared with the liver and no significant induction of PGC-1alpha could be detected at this early time point. Activation of AMPK was found in both liver and white gastrocnemius muscle as phosphorylation of Thr-172. The induction of endogenous insulin secretion by a glucose load directly after the exercise bout resulted in a significantly higher PKB/Akt phosphorylation in the liver of exercised mice. The markedly enhanced IRS-2 protein amount, and presumably reduced serine/threonine phosphorylation of the IRS proteins induced by the acute exercise could be responsible for this enhanced action of insulin. In conclusion, acute exercise induced a rapid and pronounced transcriptional adaptation in the liver, and regulated hepatic IRS proteins leading to improved cellular insulin signal transduction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone activation by type 2 deiodinase mediates exercise-induced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α expression in skeletal muscle.J Physiol. 2016 Sep 15;594(18):5255-69. doi: 10.1113/JP272440. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27302464 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of alpha-AMPK knockout on exercise-induced gene activation in mouse skeletal muscle.FASEB J. 2005 Jul;19(9):1146-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-3144fje. Epub 2005 May 5. FASEB J. 2005. PMID: 15878932
-
miRNA in the regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation to acute endurance exercise in C57Bl/6J male mice.PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5610. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005610. Epub 2009 May 19. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19440340 Free PMC article.
-
The stress response of the liver to physical exercise.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2010;16:163-83. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20839498 Review.
-
PGC-1alpha-induced improvements in skeletal muscle metabolism and insulin sensitivity.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009 Jun;34(3):307-14. doi: 10.1139/H09-008. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009. PMID: 19448691 Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise-induced regulation of key factors in substrate choice and gluconeogenesis in mouse liver.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 May;403(1-2):209-17. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2351-0. Epub 2015 Feb 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25702176
-
Low-intensity physical activity is associated with reduced risk of incident type 2 diabetes in older adults: evidence from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing.Diabetologia. 2010 Sep;53(9):1877-85. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1785-x. Epub 2010 May 22. Diabetologia. 2010. PMID: 20495973
-
Circulating levels of irisin in middle-aged first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes mellitus - correlation with pancreatic β-cell function.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014 Dec 5;6(1):133. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-6-133. eCollection 2014. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014. PMID: 25530809 Free PMC article.
-
PGC-1α in hepatic UPR during high-fat high-fructose diet and exercise training in mice.Physiol Rep. 2018 Aug;6(15):e13819. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13819. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30105901 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of gluconeogenic enzymes and 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in liver of diabetic mice after acute exercise.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2014 Oct 21;7:495-504. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S70767. eCollection 2014. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2014. PMID: 25364268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoi W, Ichiishi E, Sakamoto N, Tsujimoto A, Tokuda H, Yoshikawa T. Effect of exercise on hepatic gene expression in rats: a microarray analysis. Life Sci. 2004;75:3117–3128. - PubMed
-
- Baar K, Wende AR, Jones TE, Marison M, Nolte LA, Chen M, Kelly DP, Holloszy JO. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to exercise: rapid increase in the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. FASEB J. 2002;16:1879–1886. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum MJ. Activating AMP-activated protein kinase without AMP. Mol Cell. 2005;19:289–290. - PubMed
-
- Camacho RC, Donahue EP, James FD, Berglund ED, Wasserman DH. Energy state of the liver during short-term and exhaustive exercise in C57BL/6J mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006;290:E405–E408. - PubMed
-
- Canettieri G, Koo SH, Berdeaux R, Heredia J, Hedrick S, Zhang X, Montminy M. Dual role of the coactivator TORC2 in modulating hepatic glucose output and insulin signaling. Cell Metab. 2005;2:331–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

