Maternal renal dysfunction in sheep is associated with salt insensitivity in female offspring
- PMID: 19001051
- PMCID: PMC2670039
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.158808
Maternal renal dysfunction in sheep is associated with salt insensitivity in female offspring
Abstract
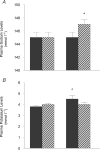
To examine the programming effects of maternal renal dysfunction (created by subtotal nephrectomy in ewes prior to mating; STNx), renal and cardiovascular function were studied in 6-month-old male and female offspring of STNx and control pregnancies. After studies were conducted on a low salt diet (LSD) some female offspring underwent salt loading (0.17 M NaCl in the drinking water for 5-7 days; HSD). On LSD both male and female offspring of STNx had similar mean arterial pressures (MAP), heart rates, cardiac outputs and renal function to those measured in offspring of control ewes. In female STNx offspring on a HSD, plasma sodium levels increased and haematocrits fell, indicating volume expansion (P < 0.05). Plasma renin levels were not suppressed despite the increases in plasma sodium concentrations, but aldosterone levels were reduced. In control animals plasma renin levels fell (P < 0.05) but there was no change in plasma aldosterone concentrations. There was a positive relationship between GFR and MAP which was present only in female STNx offspring. In conclusion, in STNx offspring there was an impaired ability to regulate glomerular filtration independent of arterial pressure, renin release was insensitive to a high salt intake and control of aldosterone secretion was abnormal. This study provides evidence of abnormal programming of the renin-angiotensin system and glomerular function in offspring of pregnancies in which there is impaired maternal renal function.
Figures



References
-
- Barker DJP. Mothers, Babies, and Disease in Later Life. London: BMJ. Medical Publishing Group; 1994.
-
- Bauer JD, Ackerman PG, Toro G. Bray's Clinical Laboratory Methods. St Louis: C. V. Mosby Co.; 1968.
-
- Boyce AC, Gibson KJ, Thomson CL, Lumbers ER. Interactions between maternal subtotal nephrectomy and salt: effects on renal function and the composition of plasma in the late gestation sheep fetus. Exp Physiol. 2008;93:262–270. - PubMed
-
- Boyce AC, Gibson KJ, Wintour EM, Koukoulas I, Lumbers ER. Effects of 7-day amino acid infusion on renal growth, function, and renin-angiotensin system in fetal sheep. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;289:R1099–R1106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

