Rad50 is dispensable for the maintenance and viability of postmitotic tissues
- PMID: 19001091
- PMCID: PMC2612516
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01525-08
Rad50 is dispensable for the maintenance and viability of postmitotic tissues
Abstract
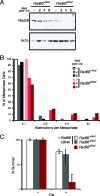
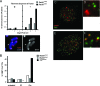
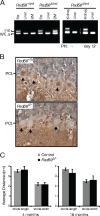
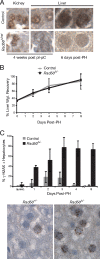
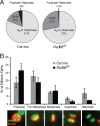
The majority of spontaneous chromosome breakage occurs during the process of DNA replication. Homologous recombination is the primary mechanism of repair of such damage, which probably accounts for the fact that it is essential for genome integrity and viability in mammalian cells. The Mre11 complex plays diverse roles in the maintenance of genomic integrity, influencing homologous recombination, checkpoint activation, and telomere maintenance. The complex is essential for cellular viability, but given its myriad influences on genomic integrity, the mechanistic basis for the nonviability of Mre11 complex-deficient cells has not been defined. In this study we generated mice carrying a conditional allele of Rad50 and examined the effects of Rad50 deficiency in proliferative and nonproliferative settings. Depletion of Rad50 in cultured cells caused extensive DNA damage and death within 3 to 5 days of Rad50 deletion. This was not associated with gross telomere dysfunction, suggesting that the telomeric functions of the Mre11 complex are not required for viability. Rad50 was also dispensable for the viability of quiescent liver and postmitotic Purkinje cells of the cerebellum. These findings support the idea that the essential functions of the Mre11 complex are associated with DNA replication and further suggest that homologous recombination is not essential in nondividing cells.
Figures
References
-
- Barlow, C., S. Hirotsune, R. Paylor, M. Liyanage, M. Eckhaus, F. Collins, Y. Shiloh, J. N. Crawley, T. Ried, D. Tagle, and A. Wynshaw-Boris. 1996. Atm-deficient mice: a paradigm of ataxia telangiectasia. Cell 86159-171. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, D. E., G. Stamp, I. Rosewell, A. Denzel, and T. Lindahl. 1998. Targeted disruption of the gene encoding DNA ligase IV leads to lethality in embryonic mice. Curr. Biol. 81395-1398. - PubMed
-
- Barski, J. J., K. Dethleffsen, and M. Meyer. 2000. Cre recombinase expression in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Genesis 2893-98. - PubMed
-
- Blindenbacher, A., X. Wang, I. Langer, R. Savino, L. Terracciano, and M. H. Heim. 2003. Interleukin 6 is important for survival after partial hepatectomy in mice. Hepatology 38674-682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
