Unconditioned behavioral effects of the powerful kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates: fast onset and entry into cerebrospinal fluid
- PMID: 19001155
- PMCID: PMC2682281
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.145342
Unconditioned behavioral effects of the powerful kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates: fast onset and entry into cerebrospinal fluid
Abstract
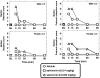
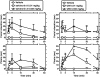
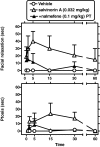
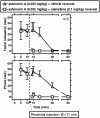
Salvinorin A is the main active component of the widely available hallucinogenic plant, Salvia divinorum. Salvinorin A is a selective high-efficacy kappa-agonist in vitro, with some unique pharmacodynamic properties. Descriptive reports show that salvinorin A-containing products produce robust behavioral effects in humans. However, these effects have not been systematically characterized in human or nonhuman primates to date. Therefore, the present studies focused on the characterization of overt effects of salvinorin A, such as sedation (operationally defined as unresponsiveness to environmental stimuli) and postural relaxation, previously observed with centrally penetrating kappa-agonists in nonhuman primates. Salvinorin A was active in these endpoints (dose range, 0.01-0.1 mg/kg i.v.) in nonhuman primates (n = 3-5), similar to the synthetic kappa-agonist U69,593 [(+)-(5alpha,7alpha,8beta)-N-methyl-N-[7-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-1-oxaspiro[4.5]-dec-8-yl]-benzeneacetamide], used for comparison herein. Salvinorin A effects could be prevented by a clinically available opioid antagonist, nalmefene (0.1 mg/kg), at doses known to block kappa-receptor-mediated effects in nonhuman primates. When injected intravenously, salvinorin A (0.032 mg/kg) could enter the central nervous system (as reflected in cisternal cerebrospinal fluid) within 1 min and reach concentrations that are in the reported range of the affinity (K(i)) of this ligand for brain kappa-receptors. Consistent with this finding, specific translationally viable behavioral effects (e.g., facial relaxation and ptosis) could also be detected within 1 to 2 min of injection of salvinorin A. These are the first studies documenting rapid unconditioned effects of salvinorin A in a primate species, consistent with descriptive reports of rapid and robust effects of this powerful hallucinogen in humans.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Behavioral effects and central nervous system levels of the broadly available κ-agonist hallucinogen salvinorin A are affected by P-glycoprotein modulation in vivo.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Jun;341(3):802-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.193227. Epub 2012 Mar 20. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22434677 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of salvinorin A, a kappa-opioid hallucinogen, on a neuroendocrine biomarker assay in nonhuman primates with high kappa-receptor homology to humans.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jan;320(1):300-6. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.112417. Epub 2006 Oct 23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17060493
-
The discriminative effects of the kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates: dissociation from classic hallucinogen effects.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 Jun;210(2):253-62. doi: 10.1007/s00213-009-1771-5. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20084367 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropharmacology of the naturally occurring kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Jun;63(2):316-47. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003244. Epub 2011 Mar 28. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21444610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salvinorin A: the "magic mint" hallucinogen finds a molecular target in the kappa opioid receptor.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Mar;24(3):107-9. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(03)00027-0. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12628350 Review.
Cited by
-
Salvinorin A decreases mortality and improves neurological outcome in a neonatal mouse hypoxia model.Transl Perioper Pain Med. 2014;1(2):9-13. Transl Perioper Pain Med. 2014. PMID: 25568887 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The G-protein biased kappa opioid agonists, triazole 1.1 and nalfurafine, produce non-uniform behavioral effects in male rhesus monkeys.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 Jun;217:173394. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2022.173394. Epub 2022 May 2. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 35513117 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of C-2 halogenated analogs of salvinorin A.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Oct 1;20(19):5749-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.08.001. Epub 2010 Aug 5. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010. PMID: 20801035 Free PMC article.
-
Studies toward the Development of Antiproliferative Neoclerodanes from Salvinorin A.J Nat Prod. 2014 Aug 22;77(8):1817-24. doi: 10.1021/np5002048. Epub 2014 Jul 30. J Nat Prod. 2014. PMID: 25075762 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Feb 3;14(2):116. doi: 10.3390/ph14020116. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33546518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baggott MJ, Erowid E, Erowid F, and Mendelson JE (2004) Use of Salvia divinorum, an unscheduled hallucinogenic plant: a web-based survey of 500 users, in College on Problems of Drug Dependence Abstract (2004 Annual Meeting); 12–17 June 2004; San Juan, Puerto Rico. College on Problems of Drug Dependence, Philadelphia.
-
- Bart G, Schluger JH, Borg L, Ho A, Bidlack JM, and Kreek MJ (2005) Nalmefene induced elevation in serum prolactin in normal human volunteers: partial kappa-opioid agonist activity? Neuropsychopharmacology 30 2254-2262. - PubMed
-
- Braida D, Limonta V, Capurro V, Fadda P, Rubino T, Mascia P, Zani A, Gori E, Fratta W, Parolaro D, and Sala M (2008) Involvement of kappa-opioid and endocannabinoid system on salvinorin A-induced reward. Biol Psychiatry 63 286-292. - PubMed
-
- Butelman ER, Harris TJ, and Kreek MJ (1999) Effects of E-2078, a stable dynorphin A(1–8) analog, on sedation and serum prolactin levels in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 147 73-80. - PubMed
-
- Butelman ER, Harris TJ, and Kreek MJ (2004) The plant-derived hallucinogen, salvinorin A, produces kappa-opioid agonist-like discriminative effects in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 172 220-224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

