TDP-43 in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 19001167
- PMCID: PMC2690860
- DOI: 10.1001/archneur.65.11.1481
TDP-43 in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
Background: Recently, TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) was identified as the major component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative neuronal and glial inclusions in the most common form of frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). It was demonstrated that different TDP-43 profiles correspond to clinical phenotypes of FTLD or ALS subgroups, and the differential diagnostic potential of TDP-43 was suggested.
Objectives: To examine TDP-43 in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and to analyze whether it could serve as a diagnostic marker.
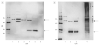
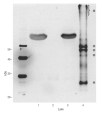
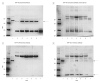
Design: We characterized CSF TDP-43 by immunoblot using different TDP-43 antibodies and determined the relative TDP-43 levels in CSF samples from patients.
Setting: Academic research.
Patients: Twelve patients with FTLD, 15 patients with ALS, 9 patients with ALS plus FTLD, 3 patients with ALS plus additional signs of frontal disinhibition, and 13 control subjects.
Main outcome measures: Results of TDP-43 immunoblot.
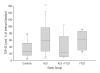
Results: Polyclonal TDP-43 antibodies recognized a 45-kDa band in all analyzed samples. Two monoclonal and N-terminus-specific antibodies did not detect any specific bands, but C-terminus-specific antibodies detected a 45-kDa band and additional bands at approximately 20 kDa in all CSF samples. Relative quantification of 45-kDa bands revealed significant differences among the diagnostic groups (P =.046). Specifically, patients with ALS (P =.03) and FTLD (P =.02) had higher TDP-43 levels than controls but with a prominent overlap of values.
Conclusion: Although there is no evidence of pathologically altered TDP-43 proteins in CSF, TDP-43 levels in CSF might aid in characterizing subgroups of patients across the ALS and FTLD disease spectrum.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The RNA-binding motif 45 (RBM45) protein accumulates in inclusion bodies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 inclusions (FTLD-TDP) patients.Acta Neuropathol. 2012 Nov;124(5):717-32. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-1045-x. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Acta Neuropathol. 2012. PMID: 22993125 Free PMC article.
-
Increased TDP-43 protein in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Acta Neuropathol. 2009 Jan;117(1):55-62. doi: 10.1007/s00401-008-0456-1. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Acta Neuropathol. 2009. PMID: 18989684
-
Differential diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from Guillain-Barré syndrome by quantitative determination of TDP-43 in cerebrospinal fluid.Int J Neurosci. 2014 May;124(5):344-9. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2013.848440. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Int J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24066851
-
Possible concurrence of TDP-43, tau and other proteins in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Neuropathology. 2018 Feb;38(1):72-81. doi: 10.1111/neup.12428. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Neuropathology. 2018. PMID: 28960544 Review.
-
Towards a TDP-43-Based Biomarker for ALS and FTLD.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;55(10):7789-7801. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0947-6. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29460270 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ALS and Frontotemporal Dysfunction: A Review.Neurol Res Int. 2012;2012:806306. doi: 10.1155/2012/806306. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Neurol Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22919484 Free PMC article.
-
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Current Status in Diagnostic Biomarkers.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1195:179-187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32633-3_26. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32468476 Review.
-
CSF Diagnostics: A Potentially Valuable Tool in Neurodegenerative and Inflammatory Disorders Involving Motor Neurons: A Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Aug 24;11(9):1522. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11091522. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in frontotemporal lobar degenerations--progress and challenges.Prog Neurobiol. 2011 Dec;95(4):636-48. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.04.012. Epub 2011 Apr 30. Prog Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21554923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concentrations of beta-amyloid precursor protein processing products in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009 Sep;116(9):1169-78. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0271-4. Epub 2009 Aug 1. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009. PMID: 19649690
References
-
- Josephs KA, Holton JL, Rossor MN, et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration and ubiquitin immunohistochemistry. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2004;30(4):369–373. - PubMed
-
- Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314(5796):130–133. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(3):602–611. - PubMed
-
- Johnson JK, Diehl J, Mendez MF, et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: demographic characteristics of 353 patients. Arch Neurol. 2005;62(6):925–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

