Polyphosphate-dependent synthesis of ATP and ADP by the family-2 polyphosphate kinases in bacteria
- PMID: 19001261
- PMCID: PMC2584756
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0807563105
Polyphosphate-dependent synthesis of ATP and ADP by the family-2 polyphosphate kinases in bacteria
Abstract
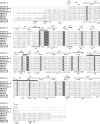
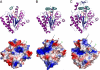
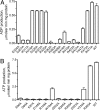
Inorganic polyphosphate (polyP) is a linear polymer of tens or hundreds of phosphate residues linked by high-energy bonds. It is found in all organisms and has been proposed to serve as an energy source in a pre-ATP world. This ubiquitous and abundant biopolymer plays numerous and vital roles in metabolism and regulation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, but the underlying molecular mechanisms for most activities of polyP remain unknown. In prokaryotes, the synthesis and utilization of polyP are catalyzed by 2 families of polyP kinases, PPK1 and PPK2, and polyphosphatases. Here, we present structural and functional characterization of the PPK2 family. Proteins with a single PPK2 domain catalyze polyP-dependent phosphorylation of ADP to ATP, whereas proteins containing 2 fused PPK2 domains phosphorylate AMP to ADP. Crystal structures of 2 representative proteins, SMc02148 from Sinorhizobium meliloti and PA3455 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, revealed a 3-layer alpha/beta/alpha sandwich fold with an alpha-helical lid similar to the structures of microbial thymidylate kinases, suggesting that these proteins share a common evolutionary origin and catalytic mechanism. Alanine replacement mutagenesis identified 9 conserved residues, which are required for activity and include the residues from both Walker A and B motifs and the lid. Thus, the PPK2s represent a molecular mechanism, which potentially allow bacteria to use polyP as an intracellular energy reserve for the generation of ATP and survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
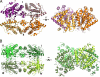

References
-
- Kornberg A, Rao NN, Ault-Riche D. Inorganic polyphosphate: A molecule of many functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:89–125. - PubMed
-
- Kulaev IS, Vagabov VM. Polyphosphate metabolism in microorganisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:83–171. - PubMed
-
- Brown MR, Kornberg A. The long and short of it: Polyphosphate, PPK, and bacterial survival. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:284–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

