The phosphotyrosine interactome of the insulin receptor family and its substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2
- PMID: 19001411
- PMCID: PMC2649814
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M800407-MCP200
The phosphotyrosine interactome of the insulin receptor family and its substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2
Abstract
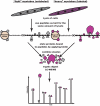
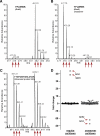
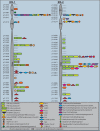
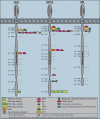
The insulin signaling pathway is critical in regulating glucose levels and is associated with diabetes, obesity, and longevity. A tyrosine phosphorylation cascade creates docking sites for protein interactions, initiating subsequent propagation of the signal throughout the cell. The phosphotyrosine interactome of this medically important pathway has not yet been studied comprehensively. We therefore applied quantitative interaction proteomics to exhaustively profile all potential phosphotyrosine-dependent interaction sites in its key players. We targeted and compared insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 (IRS-1 and IRS-2) as central distributors of the insulin signal, the insulin receptor, the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, and the insulin receptor-related receptor. Using the stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) approach with phosphorylated versus non-phosphorylated bait peptides, we found phosphorylation-specific interaction partners for 52 out of 109 investigated sites. In addition, doubly and triply phosphorylated motifs provided insight into the combinatorial effects of phosphorylation events in close proximity to each other. Our results retrieve known interactions and substantially broaden the spectrum of potential interaction partners of IRS-1 and IRS-2. A large number of common interactors rationalize their extensive functional redundancy. However, several proteins involved in signaling and metabolism interact differentially with IRS-1 and IRS-2 and thus provide leads into their different physiological roles. Differences in interactions at the receptor level are reflected in multisite recruitment of SHP2 by the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and limited but exclusive interactions with the IRR. In common with other recent reports, our data furthermore hint at non-SH2 or phosphotyrosine-binding domain-mediated phosphotyrosine binding.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction of insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) with the insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors. Evidence for two distinct phosphotyrosine-dependent interaction domains within IRS-2.J Biol Chem. 1996 May 17;271(20):11641-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.20.11641. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8662806
-
Insulin receptor substrate-2 binds to the insulin receptor through its phosphotyrosine-binding domain and through a newly identified domain comprising amino acids 591-786.J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 15;271(11):5980-3. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.11.5980. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8626379
-
Identification of a NPXY motif in growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (Grb14) and its interaction with the phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain of IRS-1.Biochemistry. 2005 Jun 7;44(22):7929-35. doi: 10.1021/bi0500271. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15924411
-
Insulin and IGF-I signaling through the insulin receptor substrate 1.Mol Reprod Dev. 1993 Aug;35(4):346-51; discussion 351-2. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080350405. Mol Reprod Dev. 1993. PMID: 8398112 Review.
-
The new elements of insulin signaling. Insulin receptor substrate-1 and proteins with SH2 domains.Diabetes. 1993 May;42(5):643-50. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.5.643. Diabetes. 1993. PMID: 8387037 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Insulin Receptor Substrate Proteins in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Asthma: New Potential Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 4;23(17):10113. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710113. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic restraint stress induces hippocampal memory deficits by impairing insulin signaling.Mol Brain. 2018 Jul 3;11(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13041-018-0381-8. Mol Brain. 2018. PMID: 29970188 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.Nature. 2014 Jun 5;510(7503):84-91. doi: 10.1038/nature13478. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24899308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the amino acids 300-600 of IRS-2 as 14-3-3 binding region with the importance of IGF-1/insulin-regulated phosphorylation of Ser-573.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043296. Epub 2012 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22912850 Free PMC article.
-
The insulin receptor family in the heart: new light on old insights.Biosci Rep. 2022 Jul 29;42(7):BSR20221212. doi: 10.1042/BSR20221212. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35766350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schlessinger, J., and Lemmon, M. A. ( 2003) SH2 and PTB domains in tyrosine kinase signaling. Sci. STKE 2003, RE12 - PubMed
-
- Pawson, T. ( 2004) Specificity in signal transduction: from phosphotyrosine-SH2 domain interactions to complex cellular systems. Cell 116, 191–203 - PubMed
-
- Huang, H., Li, L., Wu, C., Schibli, D., Colwill, K., Ma, S., Li, C., Roy, P., Ho, K., Songyang, Z., Pawson, T., Gao, Y., and Li, S. S. ( 2008) Defining the specificity space of the human SRC homology 2 domain. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 7, 768–784 - PubMed
-
- Miller, M. L., Hanke, S., Hinsby, A. M., Friis, C., Brunak, S., Mann, M., and Blom, N. ( 2008) Motif decomposition of the phosphotyrosine proteome reveals a new N-terminal binding motif for SHIP2. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 7, 181–192 - PubMed
-
- Hu, J., and Hubbard, S. R. ( 2005) Structural characterization of a novel Cbl phosphotyrosine recognition motif in the APS family of adapter proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 18943–18949 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

