Efficacy of statins in familial hypercholesterolaemia: a long term cohort study
- PMID: 19001495
- PMCID: PMC2583391
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.a2423
Efficacy of statins in familial hypercholesterolaemia: a long term cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the efficacy of statin treatment on risk of coronary heart disease in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia.
Design: Cohort study with a mean follow-up of 8.5 years.
Setting: 27 outpatient lipid clinics.
Subjects: 2146 patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia without prevalent coronary heart disease before 1 January 1990.
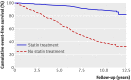
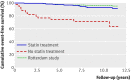
Main outcome measures: Risk of coronary heart disease in treated and "untreated" (delay in starting statin treatment) patients compared with a Cox regression model in which statin use was a time dependent variable.
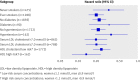
Results: In January 1990, 413 (21%) of the patients had started statin treatment, and during follow-up another 1294 patients (66%) started after a mean delay of 4.3 years. Most patients received simvastatin (n=1167, 33 mg daily) or atorvastatin (n=211, 49 mg daily). We observed an overall risk reduction of 76% (hazard ratio 0.24 (95% confidence interval 0.18 to 0.30), P<0.001). In fact, the risk of myocardial infarction in these statin treated patients was not significantly greater than that in an age-matched sample from the general population (hazard ration 1.44 (0.80 to 2.60), P=0.23).
Conclusion: Lower statin doses than those currently advised reduced the risk of coronary heart disease to a greater extent than anticipated in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia. With statin treatment, such patients no longer have a risk of myocardial infarction significantly different from that of the general population.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Comment in
-
Statins and familial hypercholesterolaemia.BMJ. 2009 Jan 21;338:a3041. doi: 10.1136/bmj.a3041. BMJ. 2009. PMID: 19158168 No abstract available.
References
-
- Austin MA, Hutter CM, Zimmern RL, Humphries SE. Familial hypercholesterolemia and coronary heart disease: a HuGE association review. Am J Epidemiol 2004;160:421-9. - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Clinical guidelines and evidence review for familial hypercholesterolaemia: the identification and management of adults and children with familial hypercholesterolaemia. 2008 (Clinical guideline 71) www.nice.org.uk/CG71
-
- Marks D, Thorogood M, Neil HA, Humphries SE. A review on the diagnosis, natural history, and treatment of familial hypercholesterolaemia. Atherosclerosis 2003;168:1-14. - PubMed
-
- Smilde TJ, van Wissen S, Wollersheim H, Trip MD, Kastelein JJ, Stalenhoef AF. Effect of aggressive versus conventional lipid lowering on atherosclerosis progression in familial hypercholesterolaemia (ASAP): a prospective, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2001;357:577-81. - PubMed
-
- Van Wissen S, Smilde TJ, Trip MD, Stalenhoef AF, Kastelein JJ. Long term safety and efficacy of high-dose atorvastatin treatment in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Am J Cardiol 2005;95:264-6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
