Changes in global gene expression in rat myometrium in transition from late pregnancy to parturition
- PMID: 19001510
- PMCID: PMC2636924
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00290.2007
Changes in global gene expression in rat myometrium in transition from late pregnancy to parturition
Abstract
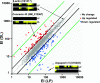
The process of parturition involves the complex interplay of factors that change the excitability and contractile activity of the uterus. We have compared the relative gene expression profile of myometrium from rats before parturition (21 days pregnant) and during delivery, using high-density DNA microarray. Of 8,740 sequences available in the array, a total of 3,782 were detected as present. From the sequences that were significantly altered, 59 genes were upregulated and 82 genes were downregulated. We were able to detect changes in genes described to have altered expression level at term, including connexin 43 and 26, cyclooxygenase 2, and oxytocin receptor, as well as novel genes that have been not previously associated with parturition. Quantitative real-time PCR on selected genes further confirmed the microarray data. Here we report for the first time that aquaporin5 (AQP5), a member of the aquaporin water channel family, was dramatically downregulated during parturition (approximately 100-fold by microarray and approximately 50-fold by real-time PCR). The emerging profile highlights biochemical cascades occurring in a period of approximately 36 h that trigger parturition and the initiation of myometrium reverse remodeling postpartum. The microarray analysis uncovered genes that were previously suspected to play a role in parturition. This regulation involves genes from immune/inflammatory response, steroid/lipid metabolism, calcium homeostasis, cell volume regulation, cell signaling, cell division, and tissue remodeling, suggesting the presence of multiple and redundant mechanisms altered in the process of birth.
Figures
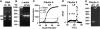
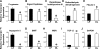

Similar articles
-
Human myometrial gene expression before and during parturition.Biol Reprod. 2005 Mar;72(3):707-19. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.032979. Epub 2004 Oct 27. Biol Reprod. 2005. PMID: 15509731 Clinical Trial.
-
Oxytocin activates NF-κB-mediated inflammatory pathways in human gestational tissues.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Mar 5;403:64-77. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25451977
-
Gene expression of estrogen and oxytocin receptors in the uterus of pregnant and parturient bitches.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015 Apr;48(4):339-43. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20143969. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 25714892 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin and parturition: a role for increased myometrial calcium and calcium sensitization?Front Biosci. 2007 Jan 1;12:619-33. doi: 10.2741/2087. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17127323 Review.
-
Myometrial oxytocin receptor expression and intracellular pathways.Minerva Ginecol. 2014 Jun;66(3):267-80. Minerva Ginecol. 2014. PMID: 24971782 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancing understanding of maternal age: correlating epigenetic clocks in blood and myometrium.Epigenetics Commun. 2022;2:3. doi: 10.1186/s43682-022-00010-0. Epub 2022 May 23. Epigenetics Commun. 2022. PMID: 36052275 Free PMC article.
-
Fluctuation of aquaporin 1, 5, and 9 expression in the pig oviduct during the estrous cycle and early pregnancy.J Histochem Cytochem. 2011 Apr;59(4):419-27. doi: 10.1369/0022155411400874. J Histochem Cytochem. 2011. PMID: 21411812 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters in reproduction: a new frontier.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Mar-Apr;22(2):164-81. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv049. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 26545808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in Aquaporin 1, 5 and 9 Gene Expression in the Porcine Oviduct According to Estrous Cycle and Early Pregnancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 16;21(8):2777. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082777. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32316329 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins during Pregnancy: Their Function and Significance.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 1;18(12):2593. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122593. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29194396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson RJ, Kudlacek PE, Clemens DL. Sulfation of minoxidil by multiple human cytosolic sulfotransferases. Chem Biol Interact 109: 53–67, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Bailey J, Sparey C, Phillips RJ, Gilmore K, Robson SC, Dunlop W, Europe-Finner GN. Expression of the cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factors, CREB, CREM and ATF2, in the human myometrium during pregnancy and labour. Mol Hum Reprod 6: 648–660, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Beggah AT, Beguin P, Bamberg K, Sachs G, Geering K. Beta-subunit assembly is essential for the correct packing and the stable membrane insertion of the H,K-ATPase alpha-subunit. J Biol Chem 274: 8217–8223, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Bethin KE, Nagai Y, Sladek R, Asada M, Sadovsky Y, Hudson TJ, Muglia LJ. Microarray analysis of uterine gene expression in mouse and human pregnancy. Mol Endocrinol 17: 1454–1469, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

