Urinary tract infections in the potential vertebroplasty patient: incidence, significance, and management
- PMID: 19001542
- PMCID: PMC7051377
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1385
Urinary tract infections in the potential vertebroplasty patient: incidence, significance, and management
Abstract
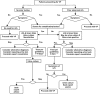
Percutaneous vertebroplasty has been deferred due to potential complications from urinary tract infections (UTIs). Our aim was to help sort out the types of treatment needed for percutaneous vertebroplasty patients and the length delay for performing the procedure. We searched for information regarding the ramifications of infection from the literature and devised a plan of treatment for the various infectious problems that may occur in patients undergoing percutaneous vertebroplasty. We devised a plan of action for the screening, testing, diagnosis and treatment of patients with a potential UTI who are presenting for a percutaneous vertebroplasty.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Updates on urinary tract infections in kidney transplantation.J Nephrol. 2019 Oct;32(5):751-761. doi: 10.1007/s40620-019-00585-3. Epub 2019 Jan 28. J Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30689126 Review.
-
The frequency and factors linked to a urinary tract infection coding in patients undergoing hip fracture surgery.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2005 Sep-Oct;6(5):316-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2005.04.005. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2005. PMID: 16165072
-
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Females and the Overlap with Overactive Bladder.Curr Urol Rep. 2018 Sep 13;19(11):94. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0839-3. Curr Urol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30215140 Review.
-
The changing epidemiology of serious bacterial infections in young infants.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Jun;33(6):595-9. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000225. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014. PMID: 24326416
-
[Urinary tract colonization and infection in critically ill patients].Med Intensiva. 2012 Mar;36(2):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.medin.2011.06.007. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Med Intensiva. 2012. PMID: 21839547 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
The efficacy of a percutaneous expandable titanium device in anatomical reduction of vertebral compression fractures of the thoracolumbar spine.Saudi Med J. 2015 Jan;36(1):52-60. doi: 10.15537/smj.2015.1.9463. Saudi Med J. 2015. PMID: 25630005 Free PMC article.
-
"Double Cross Sign" Could Be an Indicator of an Adequate Amount of Bone Cement in Kyphoplasty with the SpineJack System: A Retrospective Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 6;12(12):3068. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123068. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553075 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Appropriate Antibiotic Prescribing on Treatment Evaluation Parameters.J Public Health Afr. 2013 Jul 2;4(1):e2. doi: 10.4081/jphia.2013.e2. eCollection 2013 Jun 25. J Public Health Afr. 2013. PMID: 28299091 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration in Vertebral Compression Fractures (VCF): Effectiveness Evaluation Based on 3D Technology.J Funct Biomater. 2022 May 17;13(2):60. doi: 10.3390/jfb13020060. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35645268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfonso Olmos M, Silva Gonzalez A, Duart Clemente J, et al. Infected vertebroplasty due to uncommon bacteria solved surgically: a rare and threatening life complication of a common procedure—report of a case and a review of the literature. Spine 2006;31:E770–73 - PubMed
-
- Schmid KE, Boszczyk BM, Bierschneider M, et al. Spondylitis following vertebroplasty: a case report. Eur Spine J 2005;14:895–99 - PubMed
-
- Vats HS, McKiernan FE. Infected vertebroplasty: case report and review of literature. Spine 2006;31:E859–62 - PubMed
-
- Walker DH, Mummaneni P, Rodts GE Jr. Infected vertebroplasty: report of two cases and review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 2004;17:E6 - PubMed
-
- Yu SW, Chen WJ, Lin WC, et al. Serious pyogenic spondylitis following vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine 2004;29:E209–11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
