Cultured CD4T cells and primary human lymphocytes express hOATPs: intracellular accumulation of saquinavir and lopinavir
- PMID: 19002102
- PMCID: PMC2597246
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.320
Cultured CD4T cells and primary human lymphocytes express hOATPs: intracellular accumulation of saquinavir and lopinavir
Abstract
Background and purpose: Drug efflux tranporters (P-glycoprotein (P-gp), multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP)) limit the cellular uptake of human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors but the contribution of influx transporters in cells that (over)express P-gp or MRP is less clear. Here, we studied the expression of one influx transporter system, human organic anion-transporting polypeptide (hOATP), in some T-cell lines (CEM, CEM(VBL), CEM(E1000)) and in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and examined the effects of manipulation of influx/efflux transporters on the uptake of saquinavir and lopinavir.
Experimental approach: The expression of hOATPs was studied by PCR. We used hOATP substrate or inhibitor (estrone-3-sulphate (E-3-S) or montelukast, respectively) and inhibitors of P-gp (XR9576) and MRP (MK571 and frusemide) to study functional interactions between influx and efflux transporters in the uptake of saquinavir and lopinavir. Lipophilicity of the drugs was measured by octanol/saline partition coefficient.
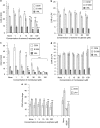
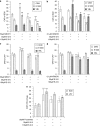
Key results: CEM cells, their variants and PBMCs express various hOATP isoforms, with OATP3A1 detected in all of the cells. MK571, XR9576 and frusemide increased the uptake of saquinavir and lopinavir. E-3-S and montelukast reduced the uptake of saquinavir and lopinavir in some, but not all, of the cells. Pretreatment of the cells with MK571, XR9576 or frusemide, followed by E-3-S co-incubation reduced the cellular accumulation of saquinavir and lopinavir. Lopinavir is much more lipophilic than saquinavir.
Conclusions and implications: Human OATPs, MRP, P-gp and lipophilicity determine the cellular uptake and retention of saquinavir and lopinavir. These data may have important implications for drug-drug interactions, drug safety and efficacy.
Figures

References
-
- Aarnoutse RE, Schapiro JM, Boucher CA, Hekster YA, Burger DM. Therapeutic drug monitoring: an aid to optimising response to antiretroviral drugs. Drugs. 2003;63:741–753. - PubMed
-
- Beck W, Mueller T, Tanzer L. Altered surface membrane glycoproteins in vinka alkaloid-resistant human leukemic lymphoblasts. Cancer Res. 1979;39:2070–2076. - PubMed
-
- Campbell SD, de Morais SM, Xu JJ. Inhibition of human organic anion transporting polypeptide OATP 1B1 as a mechanism of drug-induced hyperbilirubinemia. Chem Biol Interact. 2004;150:179–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

