Effects of levo- and dextrosimendan on NF-kappaB-mediated transcription, iNOS expression and NO production in response to inflammatory stimuli
- PMID: 19002103
- PMCID: PMC2597247
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.328
Effects of levo- and dextrosimendan on NF-kappaB-mediated transcription, iNOS expression and NO production in response to inflammatory stimuli
Abstract
Background and purpose: Levosimendan is used in the treatment of decompensated heart failure. It increases the contractility of the myocardium by sensitizing troponin C to calcium. In addition, levosimendan has been reported to have beneficial effects in experimental models of septic shock. Because heart failure and sepsis have been associated with excessive nitric oxide (NO) production through inducible NOS (iNOS), we investigated the effects of the simendans on NO production and iNOS expression and on generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
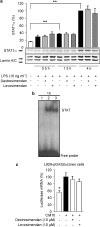
Experimental approach: Macrophages and fibroblasts were exposed to inflammatory stimuli to induce iNOS expression. Proteins were measured by western blot and mRNA expression was determined by quantitative RT-PCR. Promoter activity and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and the gamma-activated site (GAS; binding site for signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; STAT1)-mediated transcription were investigated using luciferase reporter constructs. Cytokines tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were measured by ELISA.
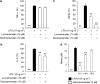
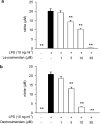
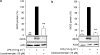
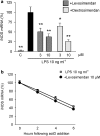
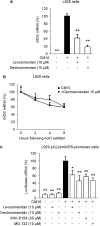
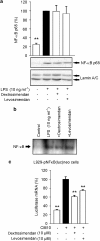
Key results: Levosimendan and dextrosimendan decreased NO production in a dose-dependent manner in cells exposed to inflammatory stimuli. The simendans decreased iNOS protein and mRNA expression but did not affect iNOS mRNA decay. These compounds decreased iNOS promoter activity and inhibited NF-kappaB-mediated transcription but not that mediated by STAT1/GAS. The simendans reduced IL-6 production slightly but they had no effect on TNF-alpha synthesis.
Conclusions and implications: The simendans downregulated NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and decreased iNOS promoter activity, iNOS expression and NO production. These mechanisms may contribute to their beneficial clinical effects.
Figures
References
-
- Avgeropoulou C, Andreadou I, Markantonis-Kyroudis S, Demopoulou M, Missovoulos P, Androulakis A, et al. The Ca(2+)-sensitizer levosimendan improves oxidative damage, BNP and pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in patients with advanced decompensated heart failure in comparison to dobutamine. Eur J Heart Fail. 2005;7:882–887. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brown RD, Ambler SK, Mitchell MD, Long CS. The cardiac fibroblast: therapeutic target in myocardial remodeling and failure. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;45:657–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

