Sex-specific genetic architecture of human disease
- PMID: 19002143
- PMCID: PMC2694620
- DOI: 10.1038/nrg2415
Sex-specific genetic architecture of human disease
Abstract
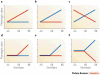
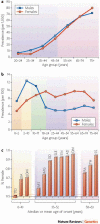
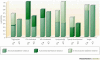
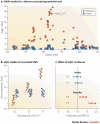
Sexual dimorphism in anatomical, physiological and behavioural traits are characteristics of many vertebrate species. In humans, sexual dimorphism is also observed in the prevalence, course and severity of many common diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases and asthma. Although sex differences in the endocrine and immune systems probably contribute to these observations, recent studies suggest that sex-specific genetic architecture also influences human phenotypes, including reproductive, physiological and disease traits. It is likely that an underlying mechanism is differential gene regulation in males and females, particularly in sex steroid-responsive genes. Genetic studies that ignore sex-specific effects in their design and interpretation could fail to identify a significant proportion of the genes that contribute to risk for complex diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Alonso LC, Rosenfield RL. Oestrogens and puberty. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;16:13–30. - PubMed
-
- Carrel L, Willard HF. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature. 2005;434:400–404. - PubMed
-
- Korstanje R, et al. Influence of sex and diet on quantitative trait loci for HDL cholesterol levels in an SM/J by NZB/BlNJ intercross population. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:881–888. - PubMed
-
- Mackay TF. The genetic architecture of quantitative traits: lessons from Drosophila. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004;14:253–257. [A classic review of gene–environment (including genotype–sex) interactions in Drosophila.] - PubMed
-
- Ueno T, et al. Rat model of familial combined hyperlipidemia as a result of comparative mapping. Physiol Genomics. 2004;17:38–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL092206/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007605/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL085197/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD021244/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL070831/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD021244/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- GM077959/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM077959/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL070831/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL07605/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL095268/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085197/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

