Artificial microRNAs as siRNA shuttles: improved safety as compared to shRNAs in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 19002161
- PMCID: PMC2834985
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2008.231
Artificial microRNAs as siRNA shuttles: improved safety as compared to shRNAs in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
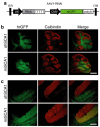
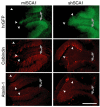
RNA interference (RNAi) provides a promising therapeutic approach to human diseases. However, data from recent reports demonstrate that short-hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) may cause cellular toxicity, and this warrants further investigation of the safety of using RNAi vectors. Earlier, in comparing hairpin-based RNAi vectors, we noted that shRNAs are highly expressed and yield an abundance of unprocessed precursors, whereas artificial microRNAs (miRNAs) are expressed at lower levels and are processed efficiently. We hypothesized that unprocessed shRNAs arise from the saturation of endogenous RNAi machinery, which poses likely a burden to cells. In this study, we tested that hypothesis by assessing the relative effects of shRNAs and artificial miRNAs on the processing and function of miRNAs. In competition assays, shRNAs disrupted miRNA biogenesis and function, whereas artificial miRNAs avoided this interference even when dosed to silence as effectively as shRNAs. We next compared the safety of these vectors in mouse cerebella, and found that shRNAs cause Purkinje cell neurotoxicity. By contrast, artificial miRNA expression was well tolerated, resulting in effective target gene silencing in Purkinje cells. These findings, together with data from earlier work in mouse striata, suggest that miRNA-based platforms are better suited for therapeutic silencing in the mammalian brain.
Figures



References
-
- McManus MT., and , Sharp PA. Gene silencing in mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:737–747. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, Xu SQ, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE., and , Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Lee YS, Nakahara K, Pham JW, Kim K, He Z, Sontheimer EJ, et al. Distinct roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer-2 in the siRNA/miRNA silencing pathways. Cell. 2004;117:69–81. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K., and , Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

