Noncanonical and canonical splice sites: a novel mutation at the rare noncanonical splice-donor cut site (IVS4+1A>G) of SEDL causes variable splicing isoforms in X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda
- PMID: 19002213
- PMCID: PMC2986207
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2008.219
Noncanonical and canonical splice sites: a novel mutation at the rare noncanonical splice-donor cut site (IVS4+1A>G) of SEDL causes variable splicing isoforms in X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda
Abstract
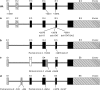
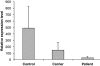
X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda can be caused by mutations in the SEDL gene. This study describes an interesting novel mutation (IVS4+1A>G) located exactly at the rare noncanonical AT-AC consensus splicing donor point of SEDL, which regained the canonical GT-AG consensus splicing junction in addition to several other rarer noncanonical splice patterns. The mutation activated several cryptic splice sites and generated the production of seven erroneous splicing isoforms, which we confirmed by sequencing of RT-PCR products and resequencing of cDNA clones. All the practical splice donors/acceptors were further assessed using FSPLICE 1.0 and SPL(M) Platforms to predict potential splice sites in genomic DNA. Subsequently, the expression levels of SEDL among the affected patients, carriers and controls were estimated using real-time quantitative PCR. Expression analyses showed that the expression levels of SEDL in both patients and carriers were decreased. Taken together, these results illustrated how disruption of the AT donor site in a rare AT-AC intron, leading to a canonical GT donor site, resulted in a multitude of aberrant transcripts, thus impairing exon definition. The unexpected splicing patterns resulting from the special mutation provide additional challenges and opportunities for understanding splicing mechanisms and specificity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effect of a novel splicing mutation (IVS2-2A-->C) of SEDL gene on RNA processing].Yi Chuan. 2005 Jul;27(4):544-8. Yi Chuan. 2005. PMID: 16120574 Chinese.
-
Mutation of acceptor splice site of the SEDL gene in X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda causes the activation of cryptic splice site.Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Jun;22(3):251-3. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15952107
-
A novel splicing mutation in the SEDL gene causes spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda in a large Chinese pedigree.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Oct 21;425:30-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23876379
-
Identification of three novel SEDL mutations, including mutation in the rare, non-canonical splice site of exon 4.Clin Genet. 2003 Sep;64(3):235-42. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0004.2003.00132.x. Clin Genet. 2003. PMID: 12919139 Review.
-
Aberrant and alternative splicing in skeletal system disease.Gene. 2013 Oct 1;528(1):21-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.06.027. Epub 2013 Jun 23. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23800666 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel deletion variant in TRAPPC2 causes spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda in a five-generation Chinese family.BMC Med Genet. 2020 May 29;21(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-01052-8. BMC Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 32471379 Free PMC article.
-
A TNXB splice donor site variant as a cause of hypermobility type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021 Feb;9(2):e1556. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1556. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021. PMID: 33332743 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing and its impact as a cancer diagnostic marker.Genomics Inform. 2012 Jun;10(2):74-80. doi: 10.5808/GI.2012.10.2.74. Epub 2012 Jun 30. Genomics Inform. 2012. PMID: 23105933 Free PMC article.
-
McSplicer: a probabilistic model for estimating splice site usage from RNA-seq data.Bioinformatics. 2021 Aug 4;37(14):2004–2011. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab050. Epub 2021 Jan 30. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33515239 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing mutations in human genetic disorders: examples, detection, and confirmation.J Appl Genet. 2018 Aug;59(3):253-268. doi: 10.1007/s13353-018-0444-7. Epub 2018 Apr 21. J Appl Genet. 2018. PMID: 29680930 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gedeon AK, Colley A, Jamieson R, et al. Identification of the gene (SEDL) causing X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda. Nat Genet. 1999;22:400–404. - PubMed
-
- Gecz J, Hillman MA, Gedeon AK, Cox TC, Baker E, Mulley JC. Gene structure and expression study of the SEDL gene for spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda. Genomics. 2000;69:242–251. - PubMed
-
- Mumm S, Zhang X, Vacca M, D'Esposito M, Whyte MP. The sedlin gene for spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda escapes X-inactivation and contains a non-canonical splice site. Gene. 2001;273:285–293. - PubMed
-
- Mumm S, Zhang X, Gottesman GS, McAlister WH, Whyte MP. Preonset studies of spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda caused by a novel 2-base pair deletion in SEDL encoding sedlin. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16:2245–2250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

