Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles
- PMID: 19002258
- PMCID: PMC2577891
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003694
Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2010;5(3) doi: 10.1371/annotation/b15ca816-7b62-4474-a568-6b60b8959742
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNA) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate translation of mRNA and protein. Loss or enhanced expression of miRNAs is associated with several diseases, including cancer. However, the identification of circulating miRNA in healthy donors is not well characterized. Microvesicles, also known as exosomes or microparticles, circulate in the peripheral blood and can stimulate cellular signaling. In this study, we hypothesized that under normal healthy conditions, microvesicles contain miRNAs, contributing to biological homeostasis.
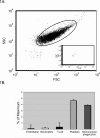
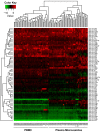
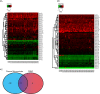
Methodology/principal findings: Microvesicles were isolated from the plasma of normal healthy individuals. RNA was isolated from both the microvesicles and matched mononuclear cells and profiled for 420 known mature miRNAs by real-time PCR. Hierarchical clustering of the data sets indicated significant differences in miRNA expression between peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and plasma microvesicles. We observed 71 miRNAs co-expressed between microvesicles and PBMC. Notably, we found 33 and 4 significantly differentially expressed miRNAs in the plasma microvesicles and mononuclear cells, respectively. Prediction of the gene targets and associated biological pathways regulated by the detected miRNAs was performed. The majority of the miRNAs expressed in the microvesicles from the blood were predicted to regulate cellular differentiation of blood cells and metabolic pathways. Interestingly, a select few miRNAs were also predicted to be important modulators of immune function.
Conclusions: This study is the first to identify and define miRNA expression in circulating plasma microvesicles of normal subjects. The data generated from this study provides a basis for future studies to determine the predictive role of peripheral blood miRNA signatures in human disease and will enable the definition of the biological processes regulated by these miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of microRNA transcriptome by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries of peripheral blood.BMC Genomics. 2010 May 7;11:288. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-288. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20459673 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional annotation analysis of their targets in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Gene. 2014 Apr 15;539(2):213-23. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.01.075. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24530307
-
Circulating MicroRNAs in Graves' Disease in Relation to Clinical Activity.Thyroid. 2016 Oct;26(10):1431-1440. doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0062. Thyroid. 2016. PMID: 27610819
-
Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in ovarian cancer.Mol Cancer. 2016 Jun 24;15(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0536-0. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27343009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis.Cancer Sci. 2010 Oct;101(10):2087-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01650.x. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20624164 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analyzing the circulating microRNAs in exosomes/extracellular vesicles from serum or plasma by qRT-PCR.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1024:129-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-453-1_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23719947 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free Circulating miRNA Biomarkers in Cancer.J Cancer. 2012;3:432-48. doi: 10.7150/jca.4919. Epub 2012 Oct 13. J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23074383 Free PMC article.
-
Commercial cow milk contains physically stable extracellular vesicles expressing immunoregulatory TGF-β.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 30;10(3):e0121123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121123. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25822997 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of circulating miRNA biomarkers based on global quantitative real-time PCR profiling.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2012 Feb 28;3(1):4. doi: 10.1186/2049-1891-3-4. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22958414 Free PMC article.
-
Selective extracellular vesicle-mediated export of an overlapping set of microRNAs from multiple cell types.BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 1;13:357. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-357. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22849433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science. 2001;294:853–858. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

