Antioxidative and anti-carcinogenic activities of tea polyphenols
- PMID: 19002670
- PMCID: PMC2820244
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-008-0372-0
Antioxidative and anti-carcinogenic activities of tea polyphenols
Abstract
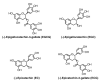
Tea (Camellia sinensis, Theaceace), a popular beverage consumed world-wide, has been studied for its preventive effects against cancer as well as cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and other diseases. Most of the proposed beneficial effects have been attributed to the polyphenolic compounds in tea, but the nature of these activities and the molecular mechanisms of their actions remain unclear. Tea polyphenols are known to be strong antioxidants. Prevention of oxidative stress, modulation of carcinogen metabolism, and prevention of DNA damage have been suggested as possible cancer preventive mechanisms for tea and tea polyphenols. In this chapter, we discuss these topics in the light of biotransformation and bioavailability of tea polyphenols. We also review the preventive effects of tea polyphenols in animal models of carcinogenesis and some of the possible post-initiation mechanisms of action. Finally, we discuss the effects of tea consumption on cancer risk in humans. It is our aim to raise some of the unanswered questions regarding cancer prevention by tea and to stimulate further research in this area.
Figures
References
-
- Auger C, Mullen W, Hara Y, Crozier A. Bioavailability of polyphenon E flavan-3-ols in humans with an ileostomy. J Nutr. 2008;138:1535S–1542S. - PubMed
-
- Balentine DA, Wiseman SA, Bouwens LC. The chemistry of tea flavonoids. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1997;37:693–704. - PubMed
-
- Bettuzzi S, Brausi M, Rizzi F, Castagnetti G, Peracchia G, Corti A. Chemoprevention of human prostate cancer by oral administration of green tea catechins in volunteers with highgrade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia: a preliminary report from a one-year proof-of-principle study. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1234–1240. - PubMed
-
- Carter O, Dashwood RH, Wang R, Dashwood WM, Orner GA, Fischer KA, Lohr CV, Pereira CB, Bailey GS, Williams DE. Comparison of white tea, green tea, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, and caffeine as inhibitors of PhIP-induced colonic aberrant crypts. Nutr Cancer. 2007;58:60–65. - PubMed
-
- Catterall F, McArdle NJ, Mitchell L, Papayanni A, Clifford MN, Ioannides C. Hepatic and intestinal cytochrome P450 and conjugase activities in rats treated with black tea theafulvins and theaflavins. Food Chem Toxicol. 2003;41:1141–1147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources