Optimized and efficient preparation of astrocyte cultures from rat spinal cord
- PMID: 19002867
- PMCID: PMC3449418
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-006-9033-4
Optimized and efficient preparation of astrocyte cultures from rat spinal cord
Abstract
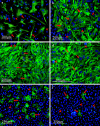
Astrocytes constitute a major class of glial cells in the CNS, and play crucial roles in physiological functioning, performance and maintenance of the CNS, as well as promotion of neuronal migration and maturation. Astrocytes have also been directly and indirectly implicated in the pathophysiology of various trauma occurrences, development of neurodegenerative diseases and nerve regeneration. To further understand mechanisms by which astrocytes elicit these effects, the first critical step in the study of astrocytes is the preparation of purified astrocytes cultures. Here we describe a simple and convenient procedure for producing rat primary astrocyte cultures of high purity, viability and proliferation. For astrocyte culture, we have optimized the isolation procedures and cultivation conditions including coating substrates, enzyme digestion, seeding density and composition of the culture medium. Using immunofluorescent antibodies against GFAP and OX-42 in combination of Hoechst 33342 fluorescent staining, we found that the purity of the astrocyte cultures was >99%. Astrocytes had high viability as measured by 3-(4, 5-dimethyl-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. In addition, flow cytometric analysis was used to measure and observe variations in the cell cycle after 1-2 passages and proliferation of astrocytes was detected with a high percentage of cells stand in S+G(2)/M phase. Therefore, the method described here is ideal for experiments, which require highly pure astrocyte cultures.
Figures



References
-
- Aronica E, Catania MV, Geurts J, Yankaya J, Troost D. Immunohistochemical localization of group I and II metabotropic glutamate receptors in control and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis human spinal cord: upregulation in reactive astrocytes. Neurosci. 2001;105:509–520. doi: 10.1016/S0306-4522(01)00181-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Gorter JA, Ijlst-Keizers H, Rozemuller AJ, Yankaya B, Leonstra Troost D. Expression and functional role of mGluR3 and mGluR5 in human astrocytes and glioma cells: opposite regulation of glutamate transporter proteins. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17:1–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02657.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

